Console
Configure Console
Conduktor Console can be configured using either a configuration file platform-config.yaml or environment variables. This is used to set up your organization's environment. Configuration can be used to declare:
- Organization name
- External database (required)
- User authentication (Basic or SSO)
- Console license
We recommend using the Console UI (Settings > Clusters page) to configure Kafka cluster, schema registry and Kafka connect. This has several advantages over the YAML configuration:
- Intuitive interface with live update capabilities
- Centralized and secured with RBAC and audit logs events
- Certificate store to help with custom certificates configuration (no more JKS files and volume mounts)
Security considerations
- The configuration file should be protected by file system permissions.
- The database should have at-rest data encryption enabled on the data volume and have limited network connectivity.
Configuration file
organization:
name: demo
admin:
email: admin@company.io
password: admin
database:
url: postgresql://conduktor:change_me@host:5432/conduktor
# OR in a decomposed way
# host: "host"
# port: 5432
# name: "conduktor"
# username: "conduktor"
# password: "change_me"
# connection_timeout: 30 # in seconds
auth:
local-users:
- email: user@conduktor.io
password: user
license: '<your license key>'
Bind file
The docker-compose below shows how to bind your platform-config.yaml file.
You can alternatively use environment variables. The CDK_IN_CONF_FILE variable is used to indicate that a configuration file is being used and the location to find it.
services:
postgresql:
image: postgres:14
hostname: postgresql
volumes:
- pg_data:/var/lib/postgresql/data
environment:
POSTGRES_DB: "conduktor"
POSTGRES_USER: "conduktor"
POSTGRES_PASSWORD: "change_me"
POSTGRES_HOST_AUTH_METHOD: "scram-sha-256"
conduktor-console:
image: conduktor/conduktor-console
depends_on:
- postgresql
ports:
- "8080:8080"
volumes:
- conduktor_data:/var/conduktor
- type: bind
source: "./platform-config.yaml"
target: /opt/conduktor/platform-config.yaml
read_only: true
environment:
CDK_IN_CONF_FILE: /opt/conduktor/platform-config.yaml
healthcheck:
test: curl -f http://localhost:8080/platform/api/modules/health/live || exit 1
interval: 10s
start_period: 10s
timeout: 5s
retries: 3
volumes:
pg_data: {}
conduktor_data: {}
Environment override
Input configuration fields can also be provided using environment variables. Here's an example of docker-compose that uses environment variables for configuration:
services:
postgresql:
image: postgres:14
hostname: postgresql
volumes:
- pg_data:/var/lib/postgresql/data
environment:
POSTGRES_DB: "conduktor"
POSTGRES_USER: "conduktor"
POSTGRES_PASSWORD: "change_me"
POSTGRES_HOST_AUTH_METHOD: "scram-sha-256"
conduktor-console:
image: conduktor/conduktor-console
depends_on:
- postgresql
ports:
- "8080:8080"
volumes:
- conduktor_data:/var/conduktor
healthcheck:
test: curl -f http://localhost:8080/platform/api/modules/health/live || exit 1
interval: 10s
start_period: 10s
timeout: 5s
retries: 3
environment:
CDK_DATABASE_URL: "postgresql://conduktor:change_me@postgresql:5432/conduktor"
CDK_LICENSE: "<your license key>"
CDK_ORGANIZATION_NAME: "demo"
CDK_ADMIN_EMAIL: "admin@company.io"
CDK_ADMIN_PASSWORD: "admin"
volumes:
pg_data: {}
conduktor_data: {}
Container user and permissions
Console is running as a non-root user conduktor-platform with UID 10001 and GID 0. All files inside the container volume /var/conduktor are owned by conduktor-platform user.
Configure memory usage
We rely on container CGroups limits and use up to 80% of the container memory limit for JVM max heap size.
-XX:+UseContainerSupport -XX:MaxRAMPercentage=80
You only need to care about the limits that you set on your container.
- Console helm
- Kubernetes
- Docker Compose
# Values.yaml
...
platform:
resources:
limits:
memory: 8Gi
...
# deployment.yaml
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
...
template:
spec:
containers:
- name: console
image: conduktor/conduktor-console
resources:
limits:
memory: 8G
...
# docker-compose.yaml
...
conduktor-console:
image: conduktor/conduktor-console
deploy:
resources:
limits:
memory: 8G
...
Configure SSL/TLS
Depending on the environment, Conduktor might need to access external services (such as Kafka clusters, SSO servers, databases or object storage) that require a custom certificate for SSL/TLS communication.
You can configure this using:
- Console UI (recommended) - you can manage your certificates in a dedicated screen and configure SSL authentication from the broker setup wizard.
- volume mount - this method is only required if you have LDAPS. Do not use it for Kafka or Kafka components.
| Kafka clusters | Schema registry / Kafka Connect | LDAPS, OIDC | |
|---|---|---|---|
| SSL to secure data in transit | UI | UI | UI |
| SSL to authenticate the client | UI | UI | Not supported |
Use the Conduktor certificate store
This option is recommended for Kafka, Kafka Connect and Schema Registry connections.
You can import and parse the certificates as text or files. The supported formats are:
- .crt
- .pem
- .jks
- .p12
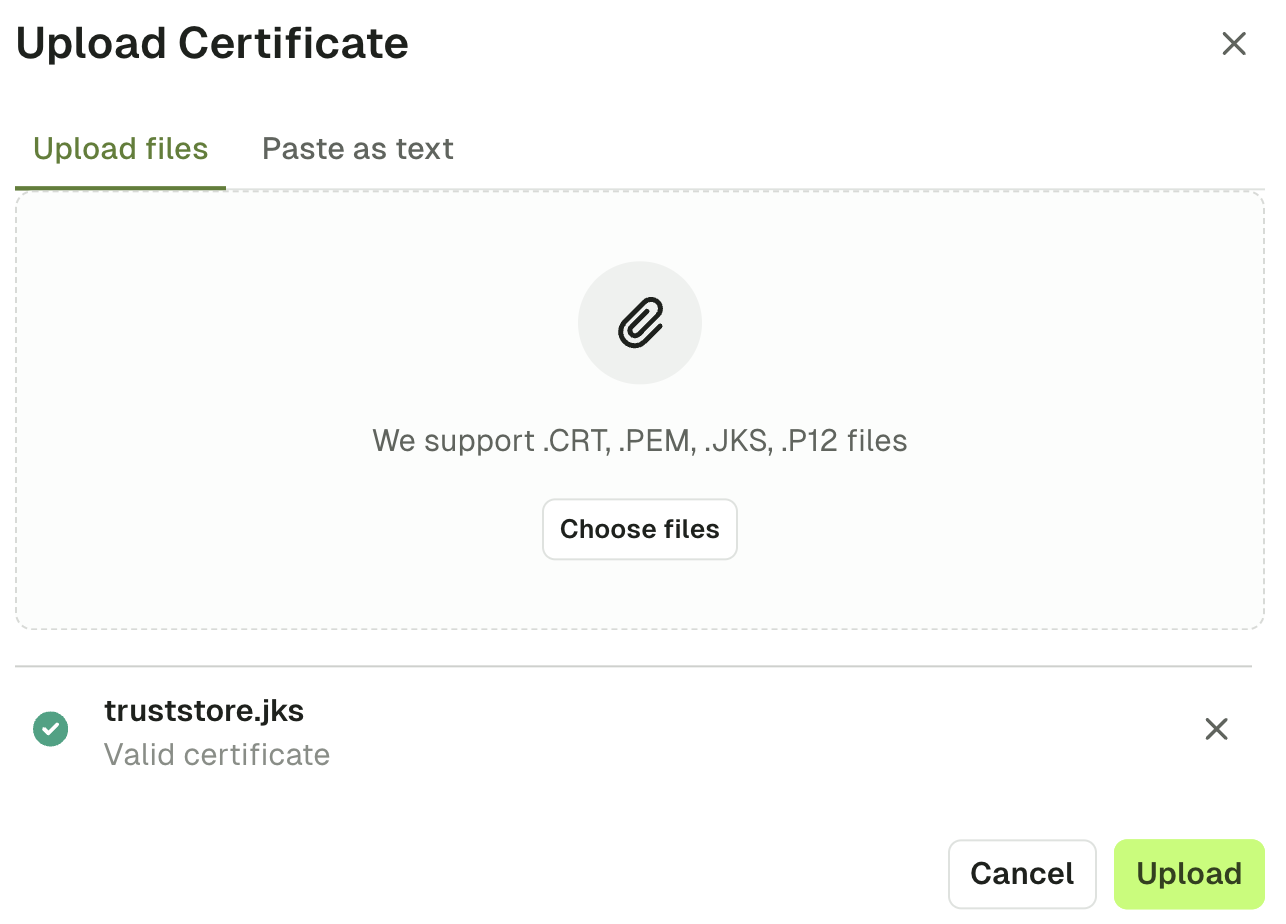
Upload certificates
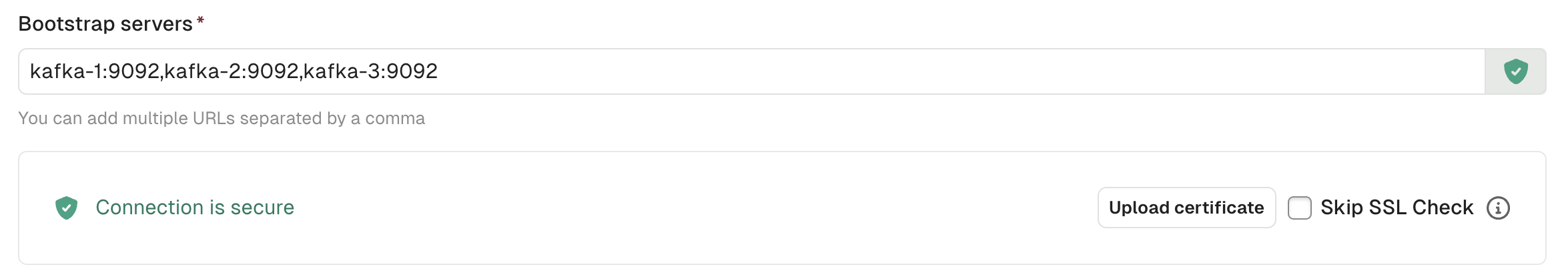
You can add cluster configurations from Settings > Clusters page. When you add the bootstrap server to your configuration, a check will be made to validate if the certificate is issued by a valid authority.
If the response indicates the certificate is not issued by a valid authority, you have two options:
- Skip SSL Check: This will skip validation of the SSL certificate on your server. This is an easy option for development environments with self-signed certificates
- Upload Certificate: This option will enable you to upload the certificate (
.crt,.pem,.jksor.p12files), or paste the certificate as text
Upon uploading the certificate, you should then see the green icon indicating the connection is secure.
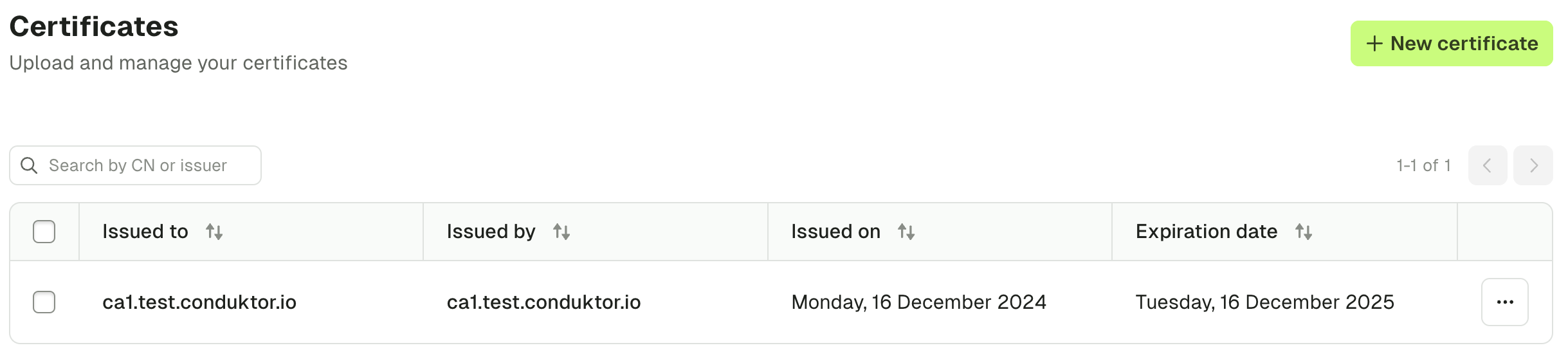
Add truststores
You can also manage organization truststores using the Settings > Certificates page. Simply add all of your certificates by uploading them or pasting them as text. In doing this, the SSL context will be derived when you configure Kafka, Kafka Connect and Schema Registry connections.
Mount custom truststore
This option is recommended for SSO, DB or other external services requiring SSL/TLS communication.
Conduktor supports SSL/TLS connections using Java truststore.
Create TrustStore (JKS) from certificate in PEM format
If you already have a truststore, you can ignore this step.
You need a keytool program that is usually packaged on JDK distributions and a certificate in PEM format (.pem or .crt).
keytool \
-importcert \
-noprompt \
-trustcacerts \
-keystore ./truststore.jks \ # Output truststore jks file
-alias "my-domain.com" \ # Certificate alias inside the truststore (usually the certificate subject)
-file ./my-certificate-file.pem \ # Input certificate file
-storepass changeit \ # Truststore password
-storetype JKS
Configure custom truststore via Conduktor Console
Mount the truststore file into the conduktor-console container and pass the correct environment variables for locating truststore file inside the container (and password, if needed).
If the truststore file is truststore.jks with password changeit, mount truststore file into /opt/conduktor/certs/truststore.jks inside the container.
If run from Docker :
docker run --rm \
--mount "type=bind,source=$PWD/truststore.jks,target=/opt/conduktor/certs/truststore.jks" \
-e CDK_SSL_TRUSTSTORE_PATH="/opt/conduktor/certs/truststore.jks" \
-e CDK_SSL_TRUSTSTORE_PASSWORD="changeit" \
conduktor/conduktor-console
From docker-compose :
services:
conduktor-console:
image: conduktor/conduktor-console
ports:
- 8080:8080
volumes:
- type: bind
source: ./truststore.jks
target: /opt/conduktor/certs/truststore.jks
read_only: true
environment:
CDK_SSL_TRUSTSTORE_PATH: '/opt/conduktor/certs/truststore.jks'
CDK_SSL_TRUSTSTORE_PASSWORD: 'changeit'
Client certificate authentication
This option is recommended for mTLS.
This mechanism uses TLS protocol to authenticate the client. Also known as:
- Mutual SSL, Mutual TLS, mTLS
- Two-Way SSL, SSL Certificate Authentication
- Digital Certificate Authentication, Public Key Infrastructure (PKI) Authentication
Use the UI (keystore method)
Use the keystore file from your Kafka admin or provider (in .jks or .p12 format).
Click the "Import from keystore" button to select a keystore file from your filesystem.
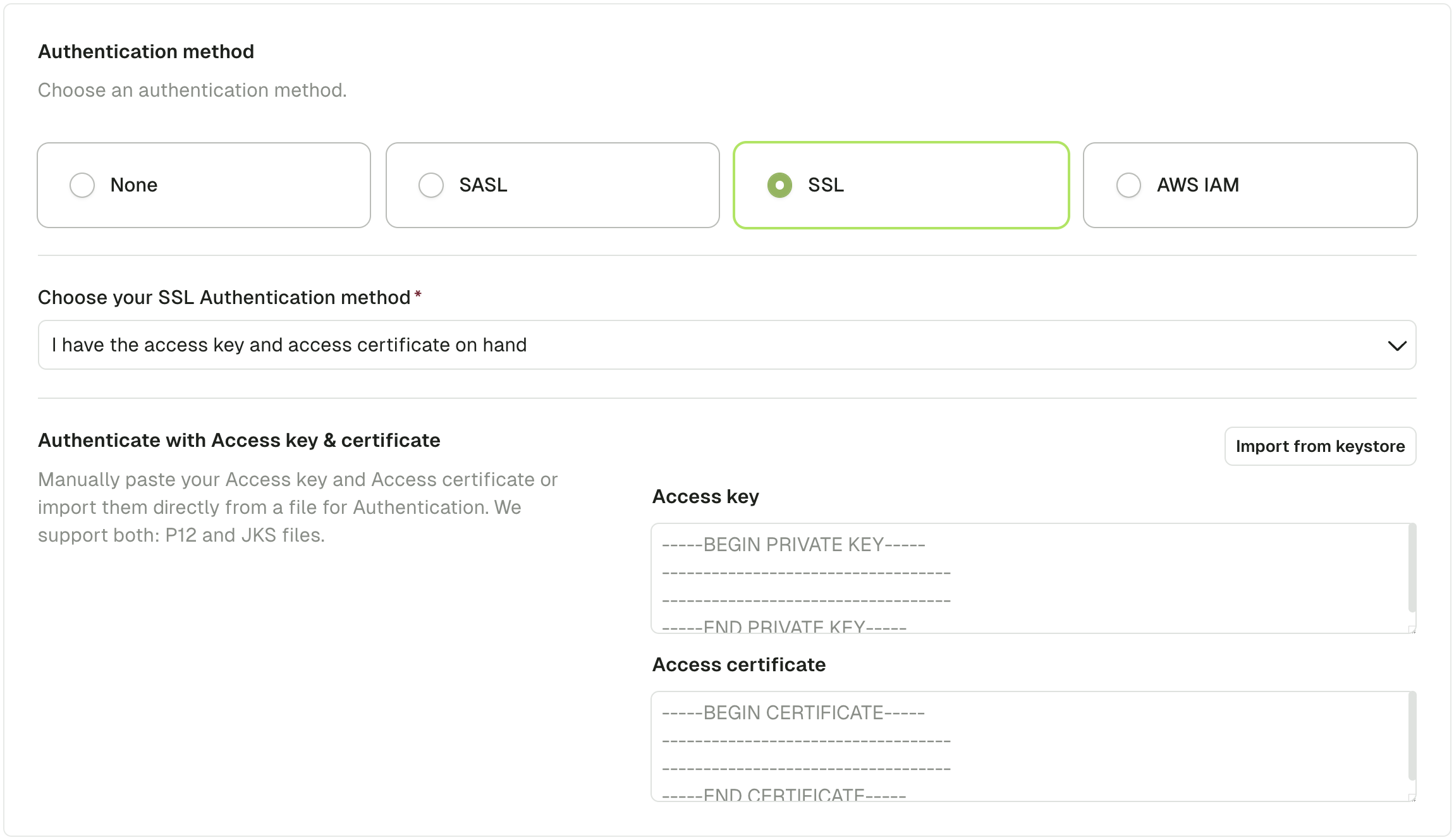
Fill in the required keystore password and key password and click "Import".
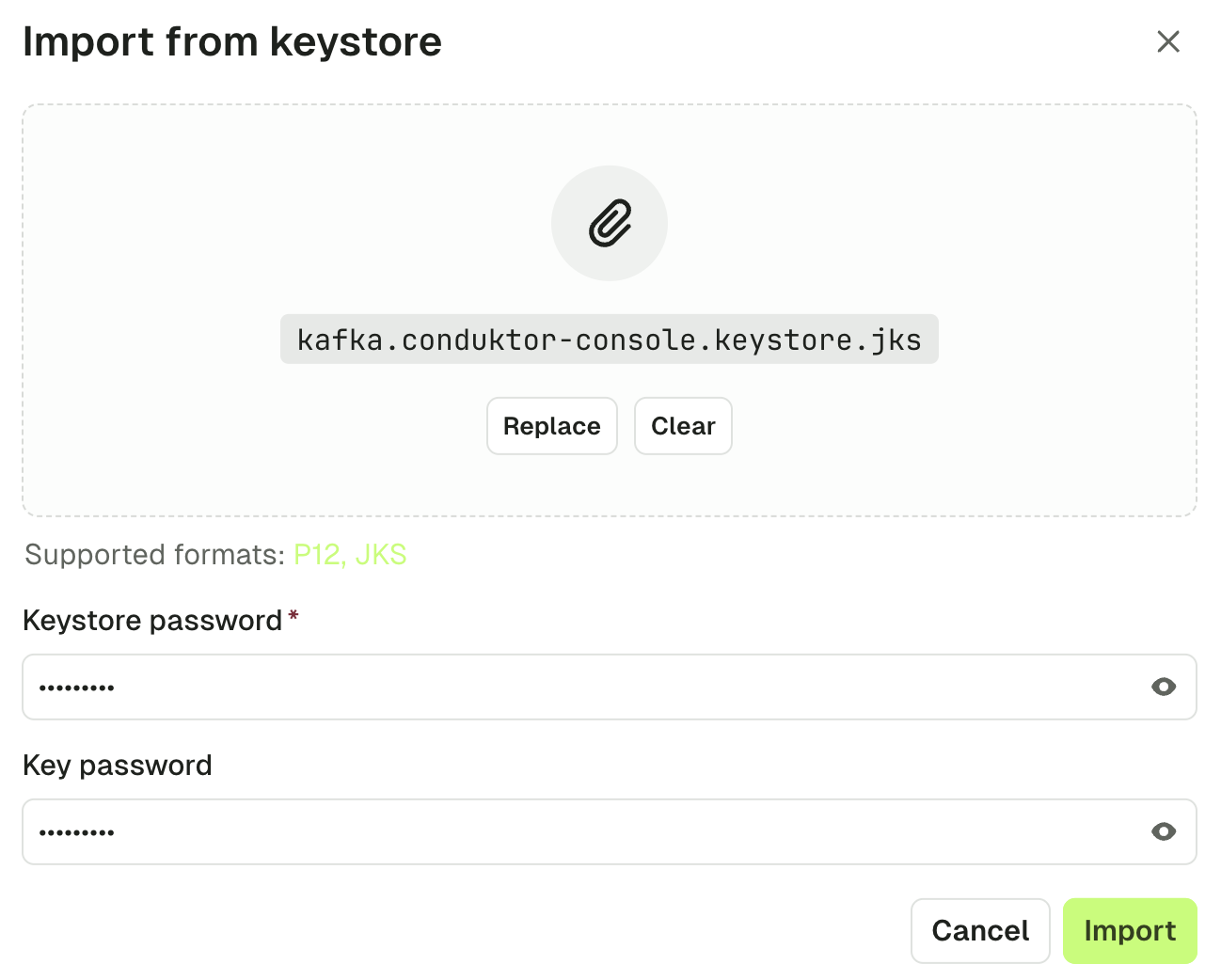
You'll get back to the cluster screen with the content of your keystore extracted into Access key and Access certificate.
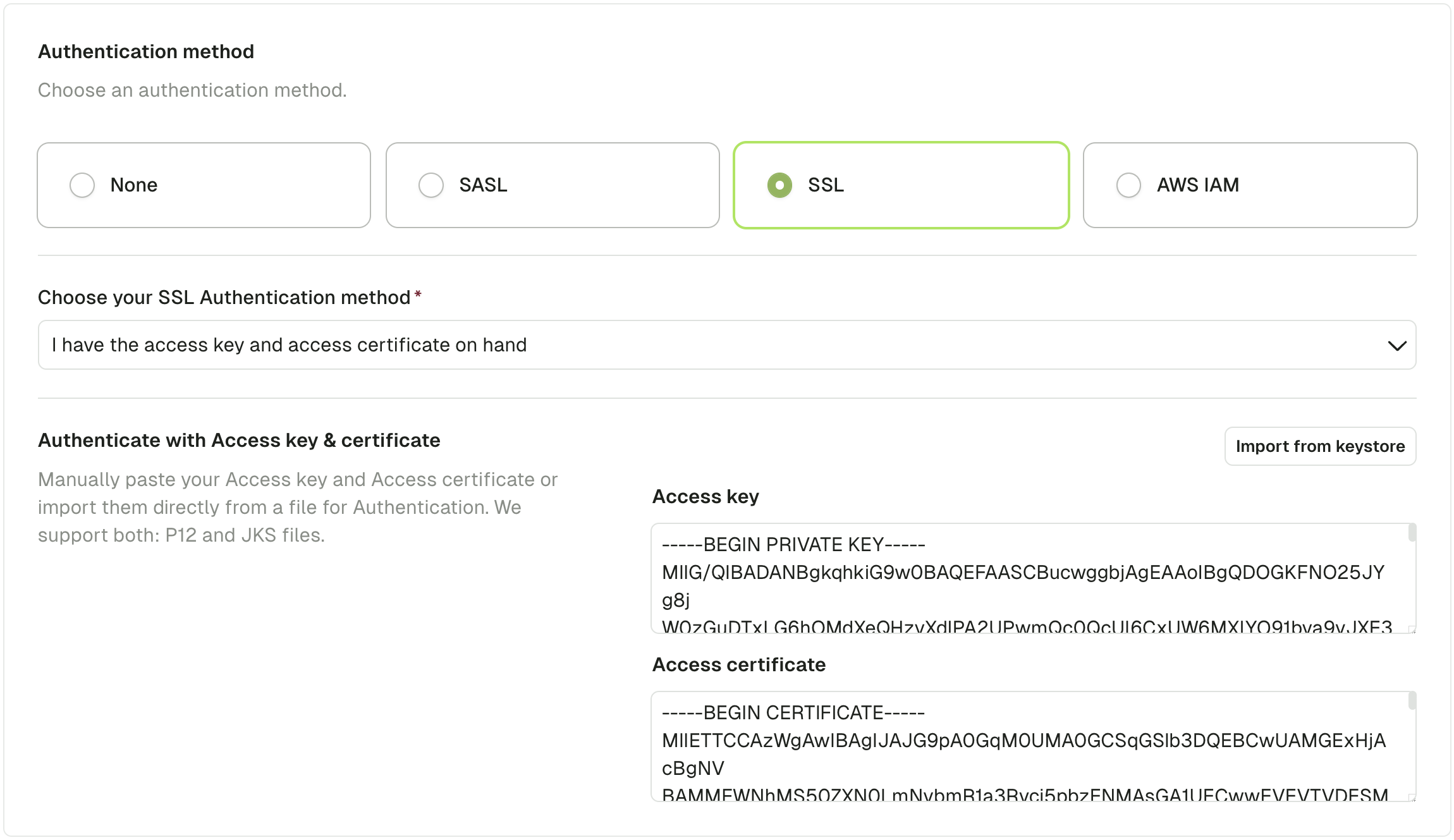
Use the UI (Access key & Access certificate method)
Your Kafka Admin or your Kafka Provider gave you 2 files for authentication.
- An Access key (
.keyfile) - An Access certificate (
.pemor.crtfile)
Here's an example with Aiven:
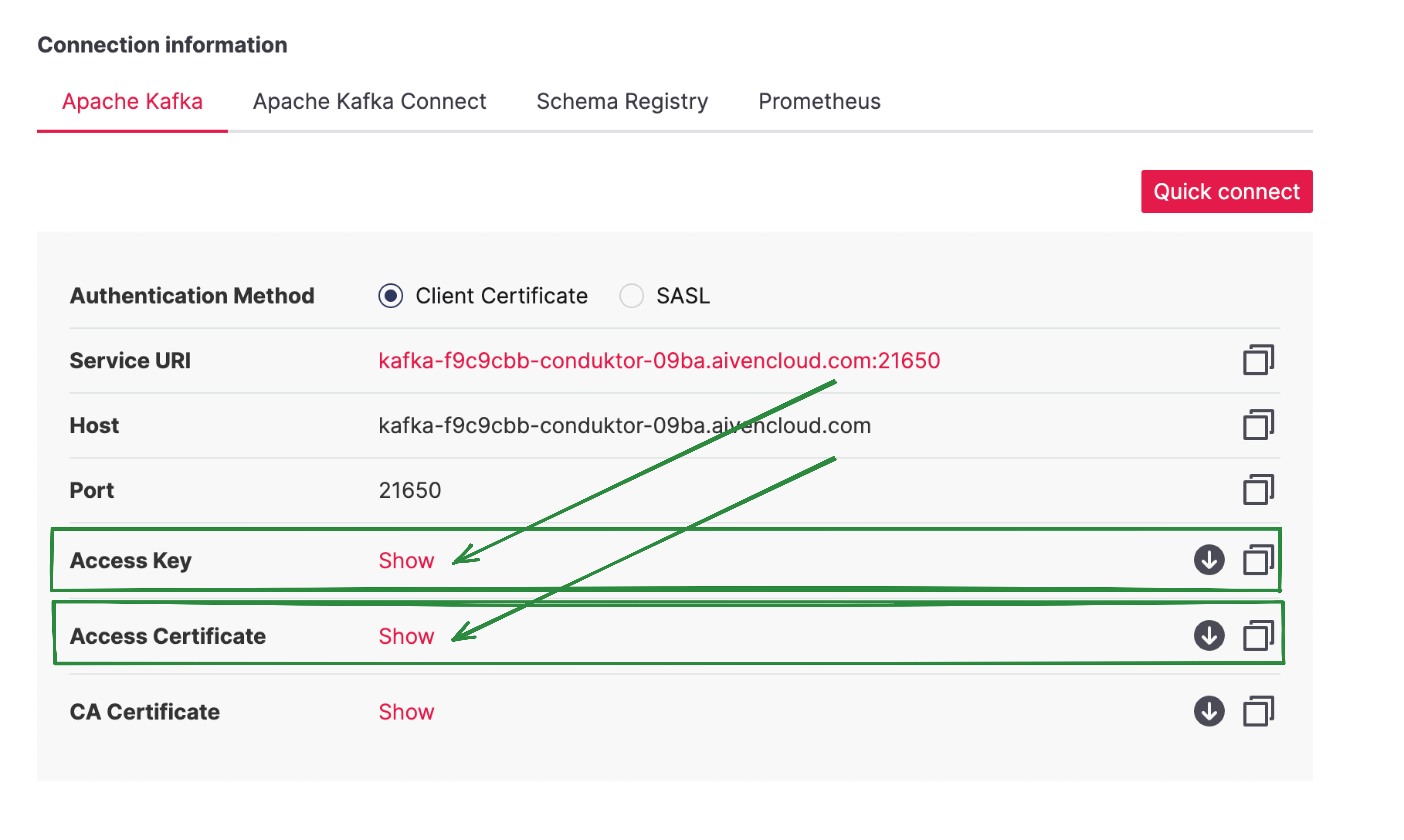
You can paste the contents of the two files into Conduktor or import from keystore.
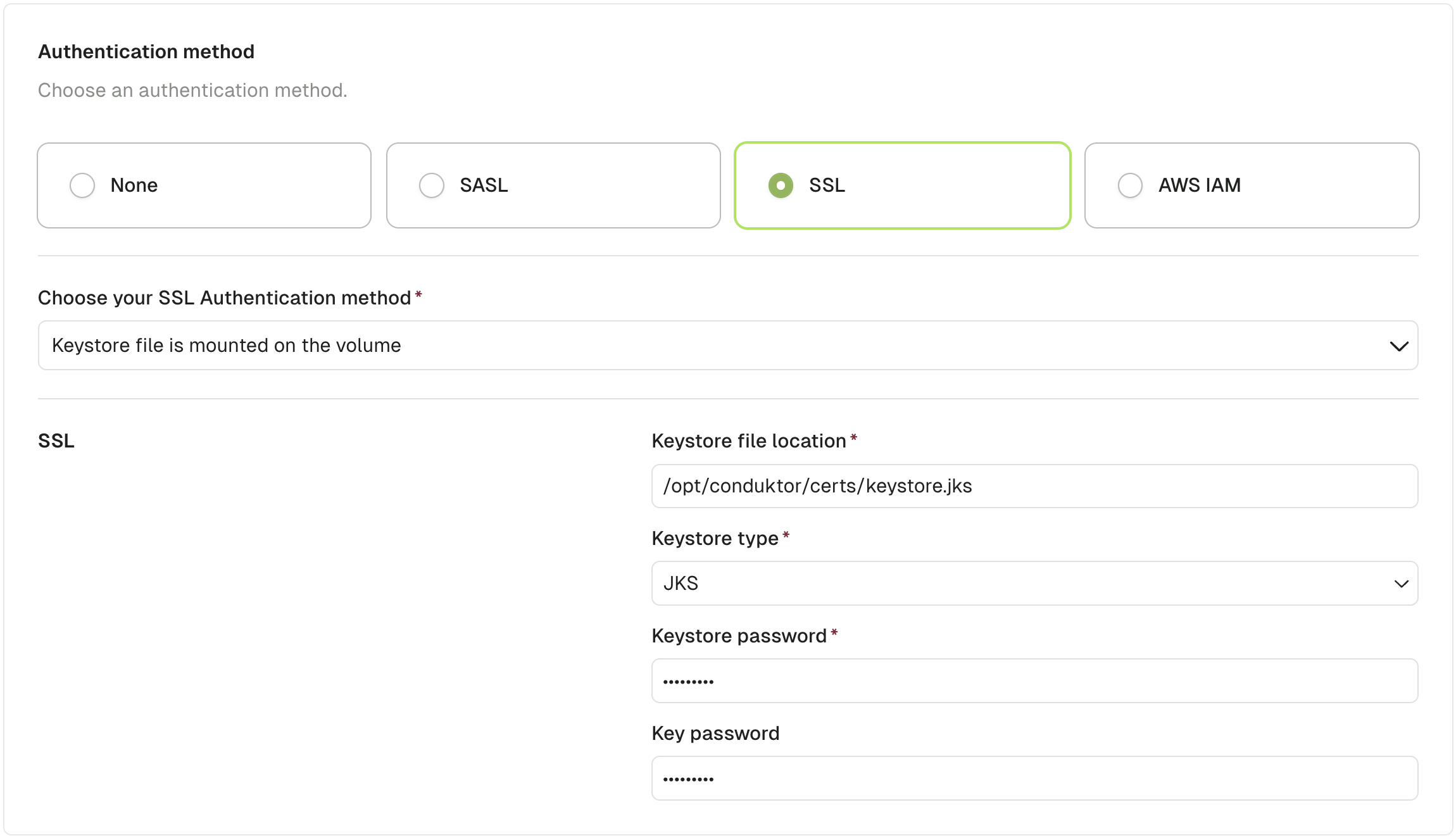
Use volume mount
You can mount the keystore file in the conduktor-console image:
services:
conduktor-console:
image: conduktor/conduktor-console
ports:
- 8080:8080
volumes:
- type: bind
source: ./keystore.jks
target: /opt/conduktor/certs/keystore.jks
read_only: true
Then from the UI, choose the SSL Authentication method Keystore file is mounted on the volume and fill in the required fields
Configure Postgres database
Conduktor Console requires a Postgres database to store its state.
Postgres requirements
- Postgres version 13 or higher
- Provided connection role should have grant
ALL PRIVILEGESon the configured database. Console should be able to create/update/delete schemas and tables on the database. - For your Postgres deployment use at least 1-2 vCPU, 1 GB of Ram, and 10 GB of disk.
If you want to use AWS RDS or AWS Aurora as a database with Console, consider the following: Console will not work with all PostgreSQL engines within RDS, it will only work with engine versions 14.8+ / 15.3+ (other versions are not fully supported).
Database configuration properties
database: is a key/value configuration consisting of:database.url: database connection url in the format[jdbc:]postgresql://[user[:password]@][[netloc][:port],...][/dbname][?param1=value1&...]database.hosts[].host: Postgresql server hosts namedatabase.hosts[].port: Postgresql server portsdatabase.host: Postgresql server host name (Deprecated. Usedatabase.hostsinstead)database.port: Postgresql server port (Deprecated. Usedatabase.hostsinstead)database.name: Database namedatabase.username: Database login roledatabase.password: Database login passworddatabase.connection_timeout: Connection timeout option in seconds
URL format
Console supports both, the standard PostgreSQL URL and JDBC PostgreSQL.
Connection username and password can be provided in the URL as basic authentication or as parameters.
database:
url: 'jdbc:postgresql://user:password@host:5432/database' # or 'postgresql://host:5432/database?user=user&password=password'
SSL support
By default, Console will try to connect to the database using SSL mode prefer. We plan to make this configurable in the future along with database certificate.
Setup
There are several options available when configuring an external database:
-
From a single connection URL
- With the
CDK_DATABASE_URLenvironment variable. - With the
database.urlconfiguration field. In either case, this connection url is using a standard PostgreSQL url in the format[jdbc:]postgresql://[user[:password]@][[netloc][:port],...][/dbname][?param1=value1&...]
- With the
-
From decomposed configuration fields
- With the
CDK_DATABASE_*env vars. - With the
database.*on configuration file.
- With the
database:
host: 'host'
port: 5432
name: 'database'
username: 'user'
password: 'password'
connection_timeout: 30 # in seconds
Example
docker run --rm \
-p "8080:8080" \
-e CDK_DATABASE_URL="postgresql://user:password@host:5432/database" \
-e LICENSE_KEY="<your-license>" \
conduktor/conduktor-console:latest
- If all connection URLs and decomposed configuration fields are provided, the decomposed configuration fields take priority.
- If an invalid connection URL or a mandatory configuration field (
host,usernameorname) is missing, Conduktor will fail gracefully with a meaningful error message. - Before Console v1.2.0, the
EMBEDDED_POSTGRES=falsewas mandatory to enable external Postgresql configuration.
Multi-host configuration
If you have a multi-host setup, you can configure the database connection with a list of hosts. Conduktor uses a PostgreSQL JDBC driver to connect to the database that supports multiple hosts in the connection url.
To configure a multi-host setup, you can use the database.url configuration field with a list of hosts separated by commas:
database:
url: 'jdbc:postgresql://user:password@host1:5432,host2:5432/database'
or with decomposed configuration fields:
database:
hosts:
- host: 'host1'
port: 5432
- host: 'host2'
port: 5432
name: 'database'
username: 'user'
password: 'password'
connection_timeout: 30 # in seconds
You can also provide JDBC connection parameter targetServerType to specify the target server type for the connection:
database:
url: 'jdbc:postgresql://user:password@host1:5432,host2:5432/database?targetServerType=primary'
Nearly all targetServerType are supported: any, primary, master, slave, secondary, preferSlave, preferSecondary and preferPrimary.
Configuration snippets
There are different options for configuring Conduktor Console. You can use:
- a YAML configuration file
- environment variables
- our API for some configurations (such as Kafka cluster configuration)
- the CLusters page in Console to configure clusters
GitOps: Manage clusters
If you want to configure clusters with a GitOps approach, we recommend using Console API.
Note that from Console v1.19, if you're configuring clusters through the YAML file, this will act as the source of truth for cluster definition. This means that if you make changes to the cluster via the UI, they will be overridden on the next restart containing a reference to your configuration file.
However, if you've created your cluster configurations using the Console UI, they will not be impacted by a restart. Removing the YAML block entirely will not remove existing clusters from the UI.
Complete configuration example
This demonstrates a complete configuration for Conduktor Enterprise consisting of one Kafka cluster with Schema Registry, SSO and license key.
For identity provider specific guides see configuring SSO. Note that if you don't have an Enterprise license, you should omit the SSO configuration and use local users instead.
- YAML file
- Environment variables
organization:
name: "conduktor"
database:
hosts:
- host: 'postgresql'
port: 5432
name: 'conduktor'
username: 'conduktor'
password: 'change_me'
connection_timeout: 30 # in seconds
monitoring:
cortex-url: 'http://conduktor-monitoring:9009/'
alert-manager-url: 'http://conduktor-monitoring:9010/'
callback-url: 'http://conduktor-console:8080/monitoring/api/'
notifications-callback-url: 'http://localhost:8080'
admin:
email: 'name@your_company.io'
password: "admin"
sso:
oauth2:
- name: 'auth0'
client-id: '<client ID>'
client-secret: '<client secret>'
openid:
issuer: 'https://<domain>'
clusters:
- id: 'confluent-pkc'
name: 'Confluent Prod'
bootstrapServers: 'pkc-lq8v7.eu-central-1.aws.confluent.cloud:9092'
properties: |
security.protocol=SASL_SSL
sasl.mechanism=PLAIN
sasl.jaas.config=org.apache.kafka.common.security.plain.PlainLoginModule required username="<username>" password="<password>";
schemaRegistry:
id: 'confluent-sr'
url: 'https://psrc-o268o.eu-central-1.aws.confluent.cloud'
security:
username: 'user'
password: 'password'
license: "" # license key if Enterprise
environment:
CDK_ORGANIZATION_NAME: 'conduktor'
CDK_LICENSE: '' # license key if Enterprise
CDK_DATABASE_URL: 'postgresql://conduktor:change_me@postgresql:5432/conduktor'
CDK_MONITORING_CORTEX-URL: 'http://conduktor-monitoring:9009/'
CDK_MONITORING_ALERT-MANAGER-URL: 'http://conduktor-monitoring:9010/'
CDK_MONITORING_CALLBACK-URL: 'http://conduktor-console:8080/monitoring/api/'
CDK_MONITORING_NOTIFICATIONS-CALLBACK-URL: 'http://localhost:8080'
CDK_ADMIN_EMAIL: 'name@your_company.io'
CDK_ADMIN_PASSWORD: 'admin'
CDK_SSO_OAUTH2_0_NAME: 'auth0'
CDK_SSO_OAUTH2_0_CLIENT-ID: '<client ID>'
CDK_SSO_OAUTH2_0_CLIENT-SECRET: '<client secret>'
CDK_SSO_OAUTH2_0_OPENID_ISSUER: 'https://<domain>'
CDK_CLUSTERS_0_ID: 'confluent-pkc'
CDK_CLUSTERS_0_NAME: 'Confluent Prod'
CDK_CLUSTERS_0_BOOTSTRAPSERVERS: 'pkc-lq8v7.eu-central-1.aws.confluent.cloud:9092'
CDK_CLUSTERS_0_PROPERTIES: "security.protocol=SASL_SSL\nsasl.mechanism=PLAIN\nsasl.jaas.config=org.apache.kafka.common.security.plain.PlainLoginModule required username=\"FY5NJX2SRXKTUBAD\" password=\"pqyHt7r+2oxIvmNCeagcpQieypHKUfvttCfNTf9Z8+sMF+cv6ai5b2KC/qmapOvC\";"
CDK_CLUSTERS_0_SCHEMAREGISTRY_ID: 'confluent-sr'
CDK_CLUSTERS_0_SCHEMAREGISTRY_URL: 'https://psrc-o268o.eu-central-1.aws.confluent.cloud'
CDK_CLUSTERS_0_SCHEMAREGISTRY_SECURITY_USERNAME: 'user'
CDK_CLUSTERS_0_SCHEMAREGISTRY_SECURITY_PASSWORD: 'password'
Plain auth example
Connect to a local cluster with no auth/encryption. For example, a local dev Kafka.
- YAML file
- Environment variables
clusters:
- id: 'local'
name: 'Local Kafka Cluster'
bootstrapServers: 'localhost:9092'
environment:
CDK_CLUSTERS_0_ID: 'local'
CDK_CLUSTERS_0_NAME: 'Local Kafka Cluster'
CDK_CLUSTERS_0_BOOTSTRAPSERVERS: 'localhost:9092'
Plain auth with schema registry
Connect to a local cluster with schema registry.
- YAML file
- Environment variables
clusters:
- id: 'local'
name: 'Local Kafka Cluster'
bootstrapServers: 'localhost:9092'
schemaRegistry:
id: 'local-sr'
url: 'http://localhost:8081'
environment:
CDK_CLUSTERS_0_ID: 'local'
CDK_CLUSTERS_0_NAME: 'Local Kafka Cluster'
CDK_CLUSTERS_0_BOOTSTRAPSERVERS: 'localhost:9092'
CDK_CLUSTERS_0_SCHEMAREGISTRY_ID: 'local-sr'
CDK_CLUSTERS_0_SCHEMAREGISTRY_URL: 'http://localhost:8081'
Kafka Connect
Cluster with Kafka Connect configured with Basic Auth.
- YAML file
- Environment variables
- id: 'kafka'
name: 'Kafka'
bootstrapServers: 'localhost:9092'
kafkaConnects:
- id: 'kafka-connect'
name: 'My Kafka Connect'
url: 'http://localhost:8083'
security:
username: '<username>'
password: '<password>'
environment:
CDK_CLUSTERS_0_ID: 'kafka'
CDK_CLUSTERS_0_NAME: 'Kafka'
CDK_CLUSTERS_0_BOOTSTRAPSERVERS: 'localhost:9092'
CDK_CLUSTERS_0_KAFKACONNECTS_0_ID: 'kafka-connect'
CDK_CLUSTERS_0_KAFKACONNECTS_0_NAME: 'My Kafka Connect'
CDK_CLUSTERS_0_KAFKACONNECTS_0_URL: 'http://localhost:8083'
CDK_CLUSTERS_0_KAFKACONNECTS_0_SECURITY_USERNAME: '<username>'
CDK_CLUSTERS_0_KAFKACONNECTS_0_SECURITY_PASSWORD: '<password>'
Amazon MSK with IAM authentication example
Connect to an MSK cluster with IAM Authentication using AWS Access Key and Secret.
Deploying this CloudFormation template to your environment might result in billable resources being consumed. See Amazon MSK pricing for details.
- YAML file
- Environment variables
clusters:
- id: 'amazon-msk-iam'
name: 'Amazon MSK IAM'
bootstrapServers: 'b-3-public.****.kafka.eu-west-1.amazonaws.com:9198'
properties: |
security.protocol=SASL_SSL
sasl.mechanism=AWS_MSK_IAM
sasl.jaas.config=software.amazon.msk.auth.iam.IAMLoginModule required;
sasl.client.callback.handler.class=io.conduktor.aws.IAMClientCallbackHandler
aws_access_key_id=<access-key-id>
aws_secret_access_key=<secret-access-key>
environment:
CDK_CLUSTERS_0_ID: 'amazon-msk-iam'
CDK_CLUSTERS_0_NAME: 'Amazon MSK IAM'
CDK_CLUSTERS_0_BOOTSTRAPSERVERS: 'b-3-public.****.kafka.eu-west-1.amazonaws.com:9198'
CDK_CLUSTERS_0_PROPERTIES: "security.protocol=SASL_SSL\nsasl.mechanism=AWS_MSK_IAM\nsasl.jaas.config=software.amazon.msk.auth.iam.IAMLoginModule required;\nsasl.client.callback.handler.class=io.conduktor.aws.IAMClientCallbackHandler\naws_access_key_id=<access-key-id>\naws_secret_access_key=<secret-access-key>"
Connect to an MSK cluster with IAM credentials inherited from environment.
- YAML file
- Environment variables
clusters:
- id: 'amazon-msk-iam'
name: 'Amazon MSK IAM'
bootstrapServers: 'b-3-public.****.kafka.eu-west-1.amazonaws.com:9198'
properties: |
security.protocol=SASL_SSL
sasl.mechanism=AWS_MSK_IAM
sasl.jaas.config=software.amazon.msk.auth.iam.IAMLoginModule required;
sasl.client.callback.handler.class=software.amazon.msk.auth.iam.IAMClientCallbackHandler
environment:
CDK_CLUSTERS_0_ID: 'amazon-msk-iam'
CDK_CLUSTERS_0_NAME: 'Amazon MSK IAM'
CDK_CLUSTERS_0_BOOTSTRAPSERVERS: 'b-3-public.****.kafka.eu-west-1.amazonaws.com:9198'
CDK_CLUSTERS_0_PROPERTIES: "security.protocol=SASL_SSL\nsasl.mechanism=AWS_MSK_IAM\nsasl.jaas.config=software.amazon.msk.auth.iam.IAMLoginModule required;\nsasl.client.callback.handler.class=software.amazon.msk.auth.iam.IAMClientCallbackHandler"
You can also override either the default profile or role.
- Override profile
- Override role
sasl.jaas.config = software.amazon.msk.auth.iam.IAMLoginModule required awsProfileName="other-profile";
sasl.jaas.config = software.amazon.msk.auth.iam.IAMLoginModule required awsRoleArn="arn:aws:iam::123456789012:role/msk_client_role";
Amazon MSK with Glue schema registry
Connect to an MSK cluster with schema registry using credentials.
- YAML file
- Environment variables
clusters:
- id: 'amazon-msk-iam'
name: 'Amazon MSK IAM'
bootstrapServers: 'b-3-public.****.kafka.eu-west-1.amazonaws.com:9198'
properties: |
security.protocol=SASL_SSL
sasl.mechanism=AWS_MSK_IAM
sasl.jaas.config=software.amazon.msk.auth.iam.IAMLoginModule required;
sasl.client.callback.handler.class=io.conduktor.aws.IAMClientCallbackHandler
aws_access_key_id=<access-key-id>
aws_secret_access_key=<secret-access-key>
schemaRegistry:
region: '<aws-region>'
security:
type: 'Credentials'
accessKeyId: '<access-key-id>'
secretKey: '<secret-key>'
environment:
CDK_CLUSTERS_0_ID: 'amazon-msk-iam'
CDK_CLUSTERS_0_NAME: 'Amazon MSK IAM'
CDK_CLUSTERS_0_BOOTSTRAPSERVERS: 'b-3-public.****.kafka.eu-west-1.amazonaws.com:9198'
CDK_CLUSTERS_0_PROPERTIES: "security.protocol=SASL_SSL\nsasl.mechanism=AWS_MSK_IAM\n
sasl.jaas.config=software.amazon.msk.auth.iam.IAMLoginModule required;\nsasl.client.callback.handler.class=io.conduktor.aws.IAMClientCallbackHandler\naws_access_key_id=<access-key-id>\naws_secret_access_key=<secret-access-key>"
CDK_CLUSTERS_0_SCHEMAREGISTRY_REGION: '<aws-region>'
CDK_CLUSTERS_0_SCHEMAREGISTRY_AMAZONSECURITY_TYPE: 'Credentials'
CDK_CLUSTERS_0_SCHEMAREGISTRY_AMAZONSECURITY_ACCESSKEYID: '<access-key-id>'
CDK_CLUSTERS_0_SCHEMAREGISTRY_AMAZONSECURITY_SECRETKEY: '<secret-key>'
Connect to an MSK cluster with schema registry using the default chain of credentials providers.
- YAML file
- Environment variables
clusters:
- id: 'amazon-msk-iam'
name: 'Amazon MSK IAM'
bootstrapServers: 'b-3-public.****.kafka.eu-west-1.amazonaws.com:9198'
properties: |
security.protocol=SASL_SSL
sasl.mechanism=AWS_MSK_IAM
sasl.jaas.config=software.amazon.msk.auth.iam.IAMLoginModule required;
sasl.client.callback.handler.class=io.conduktor.aws.IAMClientCallbackHandler
aws_access_key_id=<access-key-id>
aws_secret_access_key=<secret-access-key>
schemaRegistry:
region: '<aws-region>'
security:
type: 'FromContext'
profile: '<profile>' # optional to use the default profile
environment:
CDK_CLUSTERS_0_ID: 'amazon-msk-iam'
CDK_CLUSTERS_0_NAME: 'Amazon MSK IAM'
CDK_CLUSTERS_0_BOOTSTRAPSERVERS: 'b-3-public.****.kafka.eu-west-1.amazonaws.com:9198'
CDK_CLUSTERS_0_PROPERTIES: "security.protocol=SASL_SSL\nsasl.mechanism=AWS_MSK_IAM\n
sasl.jaas.config=software.amazon.msk.auth.iam.IAMLoginModule required;\nsasl.client.callback.handler.class=io.conduktor.aws.IAMClientCallbackHandler\naws_access_key_id=<access-key-id>\naws_secret_access_key=<secret-access-key>"
CDK_CLUSTERS_0_SCHEMAREGISTRY_REGION: '<aws-region>'
CDK_CLUSTERS_0_SCHEMAREGISTRY_AMAZONSECURITY_TYPE: 'FromContext'
CDK_CLUSTERS_0_SCHEMAREGISTRY_AMAZONSECURITY_PROFILE: '<profile>'
Connect to an MSK cluster with schema registry using a specific role.
- YAML file
- Environment variables
clusters:
- id: amazon-msk-iam
name: Amazon MSK IAM
color: #FF9900
bootstrapServers: 'b-3-public.****.kafka.eu-west-1.amazonaws.com:9198'
properties: |
security.protocol=SASL_SSL
sasl.mechanism=AWS_MSK_IAM
sasl.jaas.config=software.amazon.msk.auth.iam.IAMLoginModule required;
sasl.client.callback.handler.class=io.conduktor.aws.IAMClientCallbackHandler
aws_access_key_id=<access-key-id>
aws_secret_access_key=<secret-access-key>
schemaRegistry:
region: '<aws-region>'
security:
type: 'FromRole'
role: '<role>'
environment:
CDK_CLUSTERS_0_ID: 'amazon-msk-iam'
CDK_CLUSTERS_0_NAME: 'Amazon MSK IAM'
CDK_CLUSTERS_0_BOOTSTRAPSERVERS: 'b-3-public.****.kafka.eu-west-1.amazonaws.com:9198'
CDK_CLUSTERS_0_PROPERTIES: "security.protocol=SASL_SSL\nsasl.mechanism=AWS_MSK_IAM\n
sasl.jaas.config=software.amazon.msk.auth.iam.IAMLoginModule required;\nsasl.client.callback.handler.class=io.conduktor.aws.IAMClientCallbackHandler\naws_access_key_id=<access-key-id>\naws_secret_access_key=<secret-access-key>"
CDK_CLUSTERS_0_SCHEMAREGISTRY_REGION: '<aws-region>'
CDK_CLUSTERS_0_SCHEMAREGISTRY_AMAZONSECURITY_TYPE: 'FromRole'
CDK_CLUSTERS_0_SCHEMAREGISTRY_AMAZONSECURITY_ROLE: '<role>'
To use a specific registry for this cluster, you can add a registryName to the schemaRegistry section.
- YAML file
- Environment variables
schemaRegistry:
region: '<aws-region>'
security:
type: 'Credentials'
accessKeyId: '<access-key-id>'
secretKey: '<secret-key>'
registryName: '<registry-name>'
environment:
CDK_CLUSTERS_0_SCHEMAREGISTRY_REGION: '<aws-region>'
CDK_CLUSTERS_0_SCHEMAREGISTRY_AMAZONSECURITY_TYPE: 'Credentials'
CDK_CLUSTERS_0_SCHEMAREGISTRY_AMAZONSECURITY_ACCESSKEYID: '<access-key-id>'
CDK_CLUSTERS_0_SCHEMAREGISTRY_AMAZONSECURITY_SECRETKEY: '<secret-key>'
CDK_CLUSTERS_0_SCHEMAREGISTRY_REGISTRYNAME: '<registry-name>'
Confluent Cloud example
Connect to a Confluent cloud cluster using API keys.
- YAML file
- Environment variables
clusters:
- id: 'confluent-pkc'
name: 'Confluent Prod'
bootstrapServers: 'pkc-lzoyy.eu-central-1.aws.confluent.cloud:9092'
properties: |
security.protocol=SASL_SSL
sasl.mechanism=PLAIN
sasl.jaas.config=org.apache.kafka.common.security.plain.PlainLoginModule required username="<username>" password="<password>";
environment:
CDK_CLUSTERS_0_ID: 'confluent-pkc'
CDK_CLUSTERS_0_NAME: 'Confluent Prod'
CDK_CLUSTERS_0_BOOTSTRAPSERVERS: 'pkc-lzoyy.eu-central-1.aws.confluent.cloud:9092'
CDK_CLUSTERS_0_PROPERTIES: "security.protocol=SASL_SSL\nsasl.mechanism=PLAIN\nsasl.jaas.config=org.apache.kafka.common.security.plain.PlainLoginModule required username=\"<username>\" password=\"<password>\";"
Confluent Cloud with schema registry
Connect to a Confluent cloud cluster with schema registry using basic auth.
- YAML file
- Environment variables
- id: 'confluent-pkc'
name: 'Confluent Prod'
bootstrapServers: 'pkc-lq8v7.eu-central-1.aws.confluent.cloud:9092'
properties: |
security.protocol=SASL_SSL
sasl.mechanism=PLAIN
sasl.jaas.config=org.apache.kafka.common.security.plain.PlainLoginModule required username="<usernam>" password="<password>";
schemaRegistry:
id: 'confluent-sr'
url: 'https://psrc-o268o.eu-central-1.aws.confluent.cloud'
security:
username: '<username>'
password: '<password>'
environment:
CDK_CLUSTERS_0_ID: 'confluent-pkc'
CDK_CLUSTERS_0_NAME: 'Confluent Prod'
CDK_CLUSTERS_0_BOOTSTRAPSERVERS: 'pkc-lq8v7.eu-central-1.aws.confluent.cloud:9092'
CDK_CLUSTERS_0_PROPERTIES: "security.protocol=SASL_SSL\nsasl.mechanism=PLAIN\nsasl.jaas.config=org.apache.kafka.common.security.plain.PlainLoginModule required username=\"<username>\" password=\"<password>\";"
CDK_CLUSTERS_0_SCHEMAREGISTRY_ID: 'confluent-sr'
CDK_CLUSTERS_0_SCHEMAREGISTRY_URL: 'https://psrc-o268o.eu-central-1.aws.confluent.cloud'
CDK_CLUSTERS_0_SCHEMAREGISTRY_SECURITY_USERNAME: '<username>'
CDK_CLUSTERS_0_SCHEMAREGISTRY_SECURITY_PASSWORD: '<password>'
Confluent Cloud with service account management
Connect to a Confluent Cloud cluster and configure additional properties to manage service accounts, API keys and ACLs.
- YAML file
- Environment variables
- id: 'confluent-pkc'
name: 'Confluent Prod'
bootstrapServers: 'pkc-lq8v7.eu-central-1.aws.confluent.cloud:9092'
properties: |
security.protocol=SASL_SSL
sasl.mechanism=PLAIN
sasl.jaas.config=org.apache.kafka.common.security.plain.PlainLoginModule required username="<username>" password="<password>";
kafkaFlavor:
type: "Confluent"
key: "<api_key>" # Confluent Cloud API Key, NOT cluster API Key
secret: "<api_secret>" # Confluent Cloud API Secret, NOT cluster API Secret
confluentEnvironmentId: "<env_id>"
confluentClusterId: "<cluster_id>"
environment:
environment:
CDK_CLUSTERS_0_ID: 'confluent-pkc'
CDK_CLUSTERS_0_NAME: 'Confluent Prod'
CDK_CLUSTERS_0_BOOTSTRAPSERVERS: 'pkc-lq8v7.eu-central-1.aws.confluent.cloud:9092'
CDK_CLUSTERS_0_PROPERTIES: "security.protocol=SASL_SSL\nsasl.mechanism=PLAIN\nsasl.jaas.config=org.apache.kafka.common.security.plain.PlainLoginModule required username=\"<username>\" password=\"<password>\";"
CDK_CLUSTERS_0_KAFKAFLAVOR_TYPE: "Confluent"
CDK_CLUSTERS_0_KAFKAFLAVOR_KEY: "<api_key>"
CDK_CLUSTERS_0_KAFKAFLAVOR_SECRET: "<api_secret>"
CDK_CLUSTERS_0_KAFKAFLAVOR_CONFLUENTENVIRONMENTID: "<env_id>"
CDK_CLUSTERS_0_KAFKAFLAVOR_CONFLUENTCLUSTERID: "<cluster_id>"
SSL certificate example - Aiven (truststore)
You can use the PEM formatted files (.pem or .cer) directly by providing the CA certificate inline. Make sure the certificate is on one single line.
- YAML file
- Environment variables
- id: aiven
name: My Aiven Cluster
bootstrapServers: 'kafka-09ba.aivencloud.com:21661'
properties: |
security.protocol=SASL_SSL
sasl.mechanism=SCRAM-SHA-512
sasl.jaas.config=org.apache.kafka.common.security.scram.ScramLoginModule required username="<username>" password="<password>";
ssl.truststore.type=PEM
ssl.truststore.certificates=-----BEGIN CERTIFICATE----- <YOUR CA CERTIFICATE> -----END CERTIFICATE-----
environment:
CDK_CLUSTERS_0_ID: 'aiven'
CDK_CLUSTERS_0_NAME: 'My Aiven Cluster'
CDK_CLUSTERS_0_BOOTSTRAPSERVERS: 'kafka-09ba.aivencloud.com:21661'
CDK_CLUSTERS_0_PROPERTIES: "security.protocol=SASL_SSL\nsasl.mechanism=SCRAM-SHA-512\nsasl.jaas.config=org.apache.kafka.common.security.scram.ScramLoginModule required username=\"<username>\" password=\"<password>\";\nssl.truststore.type=PEM\nssl.truststore.certificates=-----BEGIN CERTIFICATE----- <YOUR CA CERTIFICATE> -----END CERTIFICATE-----"
Two-way SSL (keystore and truststore)
You should have three files:
- Your access key (in the keystore.jks file)
- Your access certificate (in the keystore.jks file)
- Your CA certificate (in the truststore.jks file)
Ensure the content is on a single line.
- YAML file
- Environment variables
- id: 'aiven-ssl'
name: 'Aiven SSL'
bootstrapServers: 'kafka-09ba.aivencloud.com:21650'
properties: |
security.protocol=SSL
ssl.truststore.type=PEM
ssl.truststore.certificates=-----BEGIN CERTIFICATE----- <YOUR CA CERTIFICATE> -----END CERTIFICATE-----
ssl.keystore.type=PEM
ssl.keystore.key=-----BEGIN PRIVATE KEY----- <YOUR ACCES KEY> -----END PRIVATE KEY-----
ssl.keystore.certificate.chain=-----BEGIN CERTIFICATE----- <YOUR ACCESS CERTIFICATE> -----END CERTIFICATE-----
environment:
CDK_CLUSTERS_0_ID: 'aiven-ssl'
CDK_CLUSTERS_0_NAME: 'Aiven SSL'
CDK_CLUSTERS_0_BOOTSTRAPSERVERS: 'kafka-09ba.aivencloud.com:21650'
CDK_CLUSTERS_0_PROPERTIES: "security.protocol=SSL\nssl.truststore.type=PEM\nssl.truststore.certificates=-----BEGIN CERTIFICATE----- <YOUR CA CERTIFICATE> -----END CERTIFICATE-----\nssl.keystore.type=PEM\nssl.keystore.key=-----BEGIN PRIVATE KEY----- <YOUR ACCES KEY> -----END PRIVATE KEY-----\nssl.keystore.certificate.chain=-----BEGIN CERTIFICATE----- <YOUR ACCESS CERTIFICATE> -----END CERTIFICATE-----"
Aiven with service account management
Connect to an Aiven cluster and configure additional properties to manage Service Accounts and ACLs.
- YAML file
- Environment variables
- id: 'aiven-09ba'
name: 'Aiven Prod'
bootstrapServers: 'kafka-09ba.aivencloud.com:21661'
properties: |
security.protocol=SASL_SSL
sasl.mechanism=SCRAM-SHA-512
sasl.jaas.config=org.apache.kafka.common.security.scram.ScramLoginModule required username="<username>" password="<password>";
ssl.truststore.type=PEM
ssl.truststore.certificates=-----BEGIN CERTIFICATE----- <YOUR CA CERTIFICATE> -----END CERTIFICATE-----
kafkaFlavor:
type: "Aiven"
apiToken: "<api_token>"
project: "<project>"
serviceName: "kafka-18350d67" # kafka cluster id (service name)
environment:
CDK_CLUSTERS_0_ID: 'aiven-09ba'
CDK_CLUSTERS_0_NAME: 'Aiven Prod'
CDK_CLUSTERS_0_BOOTSTRAPSERVERS: 'kafka-09ba.aivencloud.com:21661'
CDK_CLUSTERS_0_PROPERTIES: " security.protocol=SASL_SSL\n
sasl.mechanism=SCRAM-SHA-512\nsasl.jaas.config=org.apache.kafka.common.security.scram.ScramLoginModule required username="username" password="password";\nssl.truststore.type=PEM\nssl.truststore.certificates=-----BEGIN CERTIFICATE----- <YOUR CA CERTIFICATE> -----END CERTIFICATE-----"
CDK_CLUSTERS_0_KAFKAFLAVOR_TYPE: "Aiven"
CDK_CLUSTERS_0_KAFKAFLAVOR_APITOKEN: "<api_key>"
CDK_CLUSTERS_0_KAFKAFLAVOR_PROJECT: "<api_secret>"
CDK_CLUSTERS_0_KAFKAFLAVOR_SERVICENAME: "kafka-18350d67"
Conduktor Gateway virtual clusters
Configure virtual clusters with your Gateway deployment to manage Interceptors within Console.
- YAML file
- Environment variables
- id: 'kafka'
name: 'Kafka'
bootstrapServers: 'http://conduktor-proxy-internal:8888'
kafkaFlavor:
type: "Gateway"
url: "http://conduktor-proxy-internal:8888"
user: "admin"
password: "conduktor"
virtualCluster: "passthrough"
environment:
CDK_CLUSTERS_0_ID: 'aiven-09ba'
CDK_CLUSTERS_0_NAME: 'Aiven Prod'
CDK_CLUSTERS_0_BOOTSTRAPSERVERS: 'conduktor-proxy-internal:9092'
CDK_CLUSTERS_0_KAFKAFLAVOR_TYPE: "Gateway"
CDK_CLUSTERS_0_KAFKAFLAVOR_URL: "http://conduktor-proxy-internal:8888"
CDK_CLUSTERS_0_KAFKAFLAVOR_USER: "admin"
CDK_CLUSTERS_0_KAFKAFLAVOR_PASSWORD: "conduktor"
CDK_CLUSTERS_0_KAFKAFLAVOR_VIRTUALCLUSTER: "passthrough"
SASL/OAUTHBEARER and OIDC Kafka cluster example
OAUTHBEARER with OIDC Authentication is possible since Kafka 3.1 and KIP-768. To demonstrate OIDC authentication, NASA has a Kafka Cluster from which you can connect to after you sign up. Here's a config example that works for their cluster (adapt the values to your needs for your cluster).
- YAML file
- Environment variables
clusters:
- id: 'nasa'
name: 'GCN NASA Kafka'
bootstrapServers: 'kafka.gcn.nasa.gov:9092'
properties: |
security.protocol=SASL_SSL
sasl.mechanism=OAUTHBEARER
sasl.jaas.config=org.apache.kafka.common.security.oauthbearer.OAuthBearerLoginModule required \
clientId="<YOUR_CLIENT_ID>" \
clientSecret="<YOUR_CLIENT_SECRET>";
sasl.oauthbearer.token.endpoint.url=https://auth.gcn.nasa.gov/oauth2/token
sasl.login.callback.handler.class=org.apache.kafka.common.security.oauthbearer.secured.OAuthBearerLoginCallbackHandler
environment:
CDK_CLUSTERS_0_ID: 'nasa'
CDK_CLUSTERS_0_NAME: 'GCN NASA Kafka'
CDK_CLUSTERS_0_BOOTSTRAPSERVERS: 'kafka.gcn.nasa.gov:9092'
CDK_CLUSTERS_0_PROPERTIES: 'security.protocol=SASL_SSL\nsasl.mechanism=OAUTHBEARER\nsasl.jaas.config=org.apache.kafka.common.security.oauthbearer.OAuthBearerLoginModule required clientId="<YOUR_CLIENT_ID>" clientSecret="<YOUR_CLIENT_SECRET>";\nsasl.oauthbearer.token.endpoint.url=https://auth.gcn.nasa.gov/oauth2/token\nsasl.login.callback.handler.class=org.apache.kafka.common.security.oauthbearer.secured.OAuthBearerLoginCallbackHandler'
Configure Console logs
- Environment variables
- Config file
Console-wide log configuration
To configure Conduktor Console logs globally, you can use the following environment variables:
| Environment variable | Default value | |
|---|---|---|
CDK_ROOT_LOG_LEVEL | INFO | Global Console log level, one of OFF, ERROR, WARN, INFO, DEBUG |
CDK_ROOT_LOG_FORMAT | TEXT | Log format, one of TEXT or JSON (sice 1.26.0) |
CDK_ROOT_LOG_COLOR | true | Enable color in logs when possible |
For backward compatibility, CDK_DEBUG: true is still supported and is equivalent to CDK_ROOT_LOG_LEVEL: DEBUG.
Per module log configuration
To configure Conduktor Console logs on a per-module basis, you can use the environment variables detailed below.
Possible values for all of them are: OFF, ERROR, WARN, INFO, DEBUG, and TRACE.
| Environment variable | Default value | Description |
|---|---|---|
PLATFORM_STARTUP_LOG_LEVEL | INFO | Set the setup/configuration process logs level. By default, it is set to INFO, but switches to DEBUG if CDK_ROOT_LOG_LEVEL: DEBUG. |
CONSOLE_ROOT_LOG_LEVEL | CDK_ROOT_LOG_LEVEL | Logs related to any actions done in the Console UI |
PLATFORM_API_ROOT_LOG_LEVEL | CDK_ROOT_LOG_LEVEL | Internal platform API logs (health endpoints) |
Log level inheritance
If you don't explicitly set the log level for a module, it will inherit the CDK_ROOT_LOG_LEVEL.
For instance, if you only set
CDK_ROOT_LOG_LEVEL: DEBUG
# CONSOLE_ROOT_LOG_LEVEL isn't set
Then, CONSOLE_ROOT_LOG_LEVEL will be automatically set to DEBUG.
Similarly, if you set:
CDK_ROOT_LOG_LEVEL: INFO
CONSOLE_ROOT_LOG_LEVEL: DEBUG
Then, CONSOLE_ROOT_LOG_LEVEL will still be set to DEBUG, and isn't overridden.
If you want to further customize your logging at an individual logger-level, you can use a per-module logback configuration file.
By default, all logback configuration files are in /opt/conduktor/loggers/ with READ-ONLY permissions.
At startup, Console will copy all (missing) logback configuration files from /opt/conduktor/loggers/ to /var/conduktor/configs/loggers/ directory with READ-WRITE permissions.
Because all logback configuration files are set to reload themselves every 15 seconds, you can then edit them inside the container volume in /var/conduktor/configs/loggers/ to tune log level per logger.
All logback configuration files declare some expected appenders:
| Appender name | Description |
|---|---|
STDOUT | Appender that writes logs to stdout |
STDOUT_COLOR | Appender that writes logs to stdout with color |
ASYNC_STDOUT | Appender that writes logs to stdout asynchronously |
ASYNC_STDOUT_COLOR | Appender that writes logs to stdout asynchronously with color |
Structured logging (JSON)
To enable structured logging, simply set CONSOLE_ROOT_LOG_LEVEL=JSON. The logs will be structured using following format:
{
"timestamp": "2024-06-14T10:09:25.802542476+00:00",
"level": "<log level>",
"message": "<log message>",
"logger": "<logger name>",
"thread": "<logger thread>",
"stack_trace": "<throwable>",
"mdc": {
"key": "value"
}
}
The log timestamp is encoded in ISO-8601 format. When structured logging is enabled, CDK_ROOT_LOG_COLOR is always ignored.
Runtime logger configuration API
From version 1.28.0, Conduktor Console exposes an API to change the log level of a logger at runtime. This API requires admin privileges and is available on /api/public/debug/v1/loggers.
Get all loggers and their log level
GET /api/public/debug/v1/loggers :
curl -X GET 'http://localhost:8080/api/public/debug/v1/loggers' \
-H "Authorization: Bearer $API_KEY" | jq .
That will output :
[
{
"name": "io",
"level": "INFO"
},
{
"name": "io.conduktor",
"level": "INFO"
},
{
"name": "io.conduktor.authenticator",
"level": "INFO"
},
{
"name": "io.conduktor.authenticator.ConduktorUserProfile",
"level": "INFO"
},
{
"name": "org",
"level": "INFO"
},
{
"name": "org.apache",
"level": "INFO"
},
{
"name": "org.apache.avro",
"level": "INFO"
},
...
]
Get a specific logger and its log level
GET /api/public/debug/v1/loggers/{loggerName} :
curl -X GET 'http://localhost:8080/api/public/debug/v1/loggers/io.conduktor.authenticator' \
-H "Authorization: Bearer $API_KEY" | jq .
That will output :
[
{
"name": "io.conduktor.authenticator",
"level": "INFO"
},
{
"name": "io.conduktor.authenticator.ConduktorUserProfile",
"level": "INFO"
}
...
]
The loggerName filter uses a contains so you can either use the fully qualified cardinal name or just a part of it, meaning that the filter authenticator will match io.conduktor.authenticator and io.conduktor.authenticator.ConduktorUserProfile loggers.
Set a specific logger log level
PUT /api/public/debug/v1/loggers/{loggerName}/{logLevel} :
curl -X PUT 'http://localhost:8080/api/public/debug/v1/loggers/io.conduktor.authenticator/DEBUG' \
-H "Authorization: Bearer $API_KEY" | jq .
That will output the list of loggers impacted by the update:
[
"io.conduktor.authenticator",
"io.conduktor.authenticator.ConduktorUserProfile"
...
]
Like the GET endpoint, the loggerName filter use a contains so you can either use the fully qualified cardinal name or just a part of it. The logLevel is case-insensitive and can be: TRACE, DEBUG, INFO, WARN, ERROR, OFF.
Set multiple loggers log level
PUT /api/public/debug/v1/loggers :
curl -X PUT 'http://localhost:8080/public/debug/v1/loggers' \
-H "Authorization: Bearer $API_KEY" \
--data '[
{
"name": "io.conduktor.authenticator.ConduktorUserProfile",
"level": "TRACE"
},
{
"name": "io.conduktor.authenticator.adapter",
"level": "DEBUG"
}
]' | jq .
That will output the list of loggers impacted by the update:
[
"io.conduktor.authenticator.ConduktorUserProfile",
"io.conduktor.authenticator.ConduktorUserProfile$LocalUserProfile",
"io.conduktor.authenticator.adapter",
"io.conduktor.authenticator.adapter.Http4sCacheSessionStore",
...
]
Debug Console
Conduktor Console Docker image runs on Ubuntu Linux. It runs multiple services in a single Docker container. These services are supervised by supervisord.
To troubleshoot Console:
- Verify that Console is up and running.
- Manually debug Conduktor Console.
- Check the logs and send them to our support team if necessary.
1. Verify that Conduktor is up and running
- From Docker
- Kubernetes
First, verify that all the components are running.
docker ps
NAME IMAGE COMMAND SERVICE CREATED STATUS PORTS
conduktor-console conduktor/conduktor-console:1.21.0 "/__cacert_entrypoin…" conduktor-console 10 minutes ago Up 9 minutes (healthy) 0.0.0.0:8080->8080/tcp
conduktor-monitoring conduktor/conduktor-console-cortex:1.21.0 "/opt/conduktor/scri…" conduktor-monitoring 10 minutes ago Up 10 minutes (healthy) 0.0.0.0:9009-9010->9009-9010/tcp, 0.0.0.0:9090->9090/tcp
postgres postgres:15.1 "docker-entrypoint.s…" postgres 10 minutes ago Up 10 minutes 0.0.0.0:5432->5432/tcp
If you're using an external Kafka installation and external database, you will only need to verify that the conduktor-console container is showing healthy as the STATUS.
If Console is showing an "exited" status, check the Docker logs by running the command (with the appropriate container name):
docker logs conduktor-console
You can save these logs in a file:
docker logs conduktor-console >& docker-logs-output.txt
To get the status of the Conduktor Console pod in Kubernetes, you can run the following command (with the correct namespace, if any):
kubectl get pod --namespace conduktor
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
console-instance-cortex-5d85d5cfb4-qcxhs 1/1 Running 0 2m4s
console-instance-747d5ffc7b-gcpkx 1/1 Running 0 2m4s
The pod status is available in the STATUS column.
2. Manually debug Conduktor Console
Check services within the conduktor-console container
First, we will need to invoke a shell within the conduktor-console container. For that, you can use the following commands:
- Based on container name
- Based on container ID
docker exec -it conduktor-console bash
docker exec -it fe4a5d1be98f bash
From within the container, you can verify that all expected services are started. Conduktor Console uses supervisord inside of the container to ensure various services are started:
supervisorctl status
console FATAL Exited too quickly (process log may have details)
platform_api RUNNING pid 39, uptime 0:49:39
proxy RUNNING pid 33, uptime 0:49:39
In the example mentioned above, the console did not start successfully. This indicates that we need to look at the log files to investigate the issue further.
3. Get the logs and send them to support
Logs are kept in /var/conduktor/log. You can see them using:
ls /var/conduktor/log/
console-stdout---supervisor-umscgn8w.log proxy proxy-stdout---supervisor-2gim6er7.log supervisord.log
platform_api-stdout---supervisor-cqvwnsqi.log proxy-stderr---supervisor-8i0bjkaz.log startup.log
The best here is to simply bring all the logs to your local machine (in PWD) by running:
docker compose cp conduktor-console:/var/conduktor/log .
Then send these logs to oursupport team. If you've contacted us before, log into your account and create a ticket.
Healthcheck endpoints
Liveness endpoint
/api/health/live
Returns a status HTTP 200 when Console is up.
curl -s http://localhost:8080/api/health/live
Could be used to set up probes on Kubernetes or docker-compose.
docker-compose probe setup
healthcheck:
test:
[
'CMD-SHELL',
'curl --fail http://localhost:${CDK_LISTENING_PORT:-8080}/api/health/live',
]
interval: 10s
start_period: 120s # Leave time for the psql init scripts to run
timeout: 5s
retries: 3
Kubernetes liveness probe
ports:
- containerPort: 8080
protocol: TCP
name: httpprobe
livenessProbe:
httpGet:
path: /api/health/live
port: httpprobe
initialDelaySeconds: 5
periodSeconds: 10
timeoutSeconds: 5
Readiness/startup endpoint
/api/health/ready
Returns readiness of the Console. Modules status :
NOTREADY(initial state)READY
This endpoint returns a 200 status code if Console is in a READY state. Otherwise, it returns a 503 status code if Console fails to start.
curl -s http://localhost:8080/api/health/ready
# READY
Kubernetes startup probe
ports:
- containerPort: 8080
protocol: TCP
name: httpprobe
startupProbe:
httpGet:
path: /api/health/ready
port: httpprobe
initialDelaySeconds: 30
periodSeconds: 10
timeoutSeconds: 5
failureThreshold: 30
Console versions
/api/versions
This endpoint exposes module versions used to build the Console along with the overall Console version.
curl -s http://localhost:8080/api/versions | jq .
# {
# "platform": "1.27.0",
# "platformCommit": "ed849cbd545bb4711985ce0d0c93ca8588a6b31f",
# "console": "f97704187a7122f78ddc9110c09abdd1a9f9d470",
# "console_web": "05dea2124c01dfd9479bc0eb22d9f7d8aed6911b"
# }
Configuration properties and environment variables
Docker image environment variables
| Environment variable | Description | Default Value | Since Version |
|---|---|---|---|
| Logs | |||
CDK_DEBUG | Enable Console debug logs (equivalent to CDK_ROOT_LOG_LEVEL=DEBUG) | false | 1.0.0 |
CDK_ROOT_LOG_LEVEL | Set the Console global log level (one of DEBUG, INFO, WARN, ERROR) | INFO | 1.11.0 |
CDK_ROOT_LOG_FORMAT | Set logs format (one of TEXT, JSON) | TEXT | 1.26.0 |
CDK_ROOT_LOG_COLOR | Enable ANSI colors in logs | true | 1.11.0 |
CDK_LOG_TIMEZONE | Timezone for dates in logs (in Olson timezone ID format, e.g. Europe/Paris) | TZ environment variable or UTC if TZ is not defined | 1.28.0 |
| Proxy settings | |||
CDK_HTTP_PROXY_HOST | Proxy hostname | ∅ | 1.10.0 |
CDK_HTTP_PROXY_PORT | Proxy port | 80 | 1.10.0 |
CDK_HTTP_NON_PROXY_HOSTS | List of hosts that should be reached directly, bypassing the proxy. Hosts must be separated by |, end with a * for wildcards, and not contain any /. | ∅ | 1.10.0 |
CDK_HTTP_PROXY_USERNAME | Proxy username | ∅ | 1.10.0 |
CDK_HTTP_PROXY_PASSWORD | Proxy password | ∅ | 1.10.0 |
| SSL | |||
CDK_SSL_TRUSTSTORE_PATH | Truststore file path used by Console for Kafka, SSO, S3,... clients SSL/TLS verification | ∅ | 1.5.0 |
CDK_SSL_TRUSTSTORE_PASSWORD | Truststore password (optional) | ∅ | 1.5.0 |
CDK_SSL_TRUSTSTORE_TYPE | Truststore type (optional) | jks | 1.5.0 |
CDK_SSL_DEBUG | Enable SSL/TLS debug logs | false | 1.9.0 |
| Java | |||
CDK_GLOBAL_JAVA_OPTS | Custom JAVA_OPTS parameters passed to Console | ∅ | 1.10.0 |
CONSOLE_MEMORY_OPTS | Configure Java memory options | -XX:+UseContainerSupport -XX:MaxRAMPercentage=80 | 1.18.0 |
| Console | |||
CDK_LISTENING_PORT | Console listening port | 8080 | 1.2.0 |
CDK_VOLUME_DIR | Volume directory where Console stores data | /var/conduktor | 1.0.2 |
CDK_IN_CONF_FILE | Console configuration file location | /opt/conduktor/default-platform-config.yaml | 1.0.2 |
CDK_PLUGINS_DIR | Volume directory for Custom Deserializers plugins | /opt/conduktor/plugins | 1.22.0 |
| Nginx | |||
PROXY_BUFFER_SIZE | Tune internal Nginx proxy_buffer_size | 8k | 1.16.0 |
Console properties reference
You have multiple options to configure Console: via environment variables, or via a YAML configuration file. You can find a mapping of the configuration fields in the platform-config.yaml to environment variables below.
Environment variables can be set on the container or imported from a file. When importing from a file, mount the file into the container and provide its path by setting the environment variable CDK_ENV_FILE. Use a .env file with key value pairs.
MY_ENV_VAR1=value
MY_ENV_VAR2=otherValue
The logs will confirm, Sourcing environment variables from $CDK_ENV_FILE, or warn if set and the file is not found
Warning: CDK_ENV_FILE is set but the file does not exist or is not readable.
In case you set both environment variable and YAML value for a specific field, the environment variable will take precedence.
Lists start at index 0 and are provided using _idx_ syntax.
YAML property cases
YAML configuration supports multiple case formats (camelCase/kebab-case/lowercase) for property fragments such as:
clusters[].schemaRegistry.ignoreUntrustedCertificateclusters[].schema-registry.ignore-untrusted-certificateclusters[].schemaregistry.ignoreuntrustedcertificate
All are valid and equivalent in YAML.
Environment variable conversion
At startup, Conduktor Console will merge environment variables and YAML based configuration files into one unified configuration. The conversion rules are:
- Filter for environment variables that start with
CDK_ - Remove the
CDK_prefix - Convert the variable name to lowercase
- Replace
_with.for nested properties - Replace
_[0-9]+_with[0-9].for list properties. (Lists start at index 0)
For example, the environment variables CDK_DATABASE_URL will be converted to database.url, or CDK_SSO_OAUTH2_0_OPENID_ISSUER will be converted into sso.oauth2[0].openid.issuer.
The YAML equivalent would be:
database:
url: "..."
sso:
oauth2:
- openid:
issuer: "..."
When converting environment variables to YAML configuration, environment variables in UPPER-KEBAB-CASE will be converted to kebab-case in the YAML configuration.
Conversion edge cases
Because of YAML multiple case formats support, the conversion rules have some edge cases when trying to mix environment variables and YAML configuration.
Extra rules when mixing environment variables and YAML configuration:
- Don't use
camelCasein YAML configuration. Usekebab-caseorlowercase - Stick to one compatible case format for a given property fragment using the following compatibility matrix
Compatibility matrix:
| YAML\Environment | UPPER-KEBAB-CASE | UPPERCASE |
|---|---|---|
kebab-case | ✅ | 🚫 |
lowercase | 🚫 | ✅ |
camelCase | 🚫 | 🚫 |
For example, CDK_CLUSTERS_0_SCHEMAREGISTRY_IGNOREUNTRUSTEDCERTIFICATE environment variable:
# Is equivalent to and compatible with
clusters:
- schemaregistry:
ignoreuntrustedcertificate: true
# but not with
clusters:
- schema-registry:
ignore-untrusted-certificate: true
And CDK_CLUSTERS_0_SCHEMA-REGISTRY_IGNORE-UNTRUSTED-CERTIFICATE, that's why camelCase is not recommended in YAML configuration when mixing with environment variables.
Support of shell expansion in the YAML configuration file
Console supports shell expansion for environment variables and home tilde ~. This is useful if you have to use custom environment variables in your configuration.
For example, you can use the following syntax:
database:
url: "jdbc:postgresql://${DB_LOGIN}:${DB_PWD}@${DB_HOST}:${DB_PORT:-5432}/${DB_NAME}"
with the following environment variables:
| Environment variable | Value |
|---|---|
DB_LOGIN | usr |
DB_PWD | pwd |
DB_HOST | some_host |
DB_NAME | cdk |
This will be expanded to:
database:
url: "jdbc:postgresql://usr:pwd@some_host:5432/cdk"
If you want to escape the shell expansion, you can use the following syntax: $$. For example, if you want admin.password to be secret$123, you should set admin.password: "secret$$123".
File path environment variables
When an environment variable ending with _FILE is set to a file path, its corresponding unprefixed environment variable will be replaced with the content of that file.
For example, if you set CDK_LICENSE_FILE=/run/secrets/license, the value of CDK_LICENSE will be overridden by the content of the file located at /run/secrets/license.
The CDK_IN_CONF_FILE is not supported.
Global properties
| Property | Description | Environment variable | Mandatory | Type | Default |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
organization.name | Your organization's name | CDK_ORGANIZATION_NAME | false | string | "default" |
admin.email | Your organization's root administrator account email | CDK_ADMIN_EMAIL | true | string | ∅ |
admin.password | Your organization's root administrator account password. Must be at least 8 characters in length, and include at least 1 uppercase letter, 1 lowercase letter, 1 number, and 1 special symbol | CDK_ADMIN_PASSWORD | true | string | ∅ |
license | Enterprise license key. If not provided, fallback to free plan. | CDK_LICENSE or LICENSE_KEY | false | string | ∅ |
platform.external.url | Force Console external URL. Useful for SSO callback URL when using a reverse proxy. By default, Console will try to guess it automatically using X-Forwarded-* headers coming from upstream reverse proxy. | CDK_PLATFORM_EXTERNAL_URL | false | string | ∅ |
platform.https.cert.path | Path to the SSL certificate file | CDK_PLATFORM_HTTPS_CERT_PATH | false | string | ∅ |
platform.https.key.path | Path to the SSL private key file | CDK_PLATFORM_HTTPS_KEY_PATH | false | string | ∅ |
enable_product_metrics | In order to improve Conduktor Console, we collect anonymous usage metrics. Set to false, this configuration disable all of our metrics collection. | CDK_ENABLE_PRODUCT_METRICS | false | boolean | true |
Database properties
See database configuration for details.
| Property | Description | Environment variable | Mandatory | Type | Default |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
database.url | External PostgreSQL configuration URL in format [jdbc:]postgresql://[user[:password]@][[netloc][:port],...][/dbname][?param1=value1&...] | CDK_DATABASE_URL | false | string | ∅ |
database.hosts[].host | External PostgreSQL servers hostname | CDK_DATABASE_HOSTS_0_HOST | false | string | ∅ |
database.hosts[].port | External PostgreSQL servers port | CDK_DATABASE_HOSTS_0_PORT | false | int | ∅ |
database.host | External PostgreSQL server hostname (Deprecated, use database.hosts instead) | CDK_DATABASE_HOST | false | string | ∅ |
database.port | External PostgreSQL server port (Deprecated, use database.hosts instead) | CDK_DATABASE_PORT | false | int | ∅ |
database.name | External PostgreSQL database name | CDK_DATABASE_NAME | false | string | ∅ |
database.username | External PostgreSQL login role | CDK_DATABASE_USERNAME | false | string | ∅ |
database.password | External PostgreSQL login password | CDK_DATABASE_PASSWORD | false | string | ∅ |
database.connection_timeout | External PostgreSQL connection timeout in seconds | CDK_DATABASE_CONNECTIONTIMEOUT | false | int | ∅ |
Session lifetime properties
| Property | Description | Environment variable | Mandatory | Type | Default value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
auth.sessionLifetime | Max session lifetime in seconds | CDK_AUTH_SESSIONLIFETIME | false | int | 259200 |
auth.idleTimeout | Max idle session time in seconds (access token lifetime). Should be lower than auth.sessionLifetime | CDK_AUTH_IDLETIMEOUT | false | int | 259200 |
Local users properties
Optional local account list used to log into Console.
| Property | Description | Environment variable | Mandatory | Type | Default value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
auth.local-users[].email | User login | CDK_AUTH_LOCALUSERS_0_EMAIL | true | string | "admin@conduktor.io" |
auth.local-users[].password | User password | CDK_AUTH_LOCALUSERS_0_PASSWORD | true | string | "admin" |
Monitoring properties
To see monitoring graphs and use alerts, you have to ensure that Cortex is also deployed.
Monitoring Configuration for Console
First, we need to configure Console to connect to Cortex services. By default, Cortex ports are:
- Query port: 9009
- Alert manager port: 9010
| Property | Description | Environment variable | Mandatory | Type | Default |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
monitoring.cortex-url | Cortex Search Query URL with port 9009 | CDK_MONITORING_CORTEXURL | true | string | ∅ |
monitoring.alert-manager-url | Cortex Alert Manager URL with port 9010 | CDK_MONITORING_ALERTMANAGERURL | true | string | ∅ |
monitoring.callback-url | Console API | CDK_MONITORING_CALLBACKURL | true | string | ∅ |
monitoring.notifications-callback-url | Where the Slack notification should redirect | CDK_MONITORING_NOTIFICATIONCALLBACKURL | true | string | ∅ |
monitoring.clusters-refresh-interval | Refresh rate in seconds for metrics | CDK_MONITORING_CLUSTERREFRESHINTERVAL | false | int | 60 |
monitoring.use-aggregated-metrics | Defines whether use the new aggregated metrics in the Console graphs | CDK_MONITORING_USEAGGREGATEDMETRICS | No | Boolean | false |
monitoring.enable-non-aggregated-metrics | Toggles the collection of obsolete granular metrics | CDK_MONITORING_ENABLENONAGGREGATEDMETRICS | No | Boolean | true |
monitoring.use-aggregated-metrics and monitoring.enable-non-aggregated-metrics are temporary flags to help you transition to the new metrics collection system. They will be removed in a future release.
Swap their default value if you experience performance issues when Console is connected with large Kafka clusters:
CDK_MONITORING_USEAGGREGATEDMETRICS: true
CDK_MONITORING_ENABLENONAGGREGATEDMETRICS: false
Monitoring configuration for Cortex
See Cortex configuration for details.
SSO properties
See authentication guide for snippets.
| Property | Description | Environment variable | Mandatory | Type | Default |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
sso.ignoreUntrustedCertificate | Disable SSL checks | CDK_SSO_IGNOREUNTRUSTEDCERTIFICATE | false | boolean | false |
sso.trustedCertificates | SSL public certificates for SSO authentication (LDAPS and OAuth2) as PEM | CDK_SSO_TRUSTEDCERTIFICATES | false | string | ∅ |
LDAP properties
| Property | Description | Environment variable | Mandatory | Type | Default |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
sso.ldap[].name | Ldap connection name | CDK_SSO_LDAP_0_NAME | true | string | ∅ |
sso.ldap[].server | Ldap server host and port | CDK_SSO_LDAP_0_SERVER | true | string | ∅ |
sso.ldap[].managerDn | Sets the manager DN | CDK_SSO_LDAP_0_MANAGERDN | true | string | ∅ |
sso.ldap[].managerPassword | Sets the manager password | CDK_SSO_LDAP_0_MANAGERPASSWORD | true | string | ∅ |
sso.ldap[].search-subtree | Sets if the subtree should be searched. | CDK_SSO_LDAP_0_SEARCHSUBTREE | false | boolean | true |
sso.ldap[].search-base | Sets the base DN to search. | CDK_SSO_LDAP_0_SEARCHBASE | true | string | ∅ |
sso.ldap[].search-filter | Sets the search filter. By default, the filter is set to (uid={0}) for users using class type InetOrgPerson. | CDK_SSO_LDAP_0_SEARCHFILTER | false | string | "(uid={0})" |
sso.ldap[].search-attributes | Sets the attributes list to return. By default, all attributes are returned. Platform search for uid, cn, mail, email, givenName, sn, displayName attributes to map into user token. | CDK_SSO_LDAP_0_SEARCHATTRIBUTES | false | string array | [] |
sso.ldap[].groups-enabled | Sets if group search is enabled. | CDK_SSO_LDAP_0_GROUPSENABLED | false | boolean | false |
sso.ldap[].groups-subtree | Sets if the subtree should be searched. | CDK_SSO_LDAP_0_GROUPSSUBTREE | false | boolean | true |
sso.ldap[].groups-base | Sets the base DN to search from. | CDK_SSO_LDAP_0_GROUPSBASE | true | string | ∅ |
sso.ldap[].groups-filter | Sets the group search filter. If using group class type GroupOfUniqueNames use the filter "uniqueMember={0}". For group class GroupOfNames use "member={0}". | CDK_SSO_LDAP_0_GROUPSFILTER | false | string | "uniquemember={0}" |
sso.ldap[].groups-filter-attribute | Sets the name of the user attribute to bind to the group search filter. Defaults to the user’s DN. | CDK_SSO_LDAP_0_GROUPSFILTERATTRIBUTE | false | string | ∅ |
sso.ldap[].groups-attribute | Sets the group attribute name. Defaults to cn. | CDK_SSO_LDAP_0_GROUPSATTRIBUTE | false | string | "cn" |
sso.ldap[].properties | Additional properties that will be passed to identity provider context. | CDK_SSO_LDAP_0_PROPERTIES | false | dictionary | ∅ |
OAuth2 properties
| Property | Description | Environment variable | Mandatory | Type | Default |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
sso.oauth2[].name | OAuth2 connection name | CDK_SSO_OAUTH2_0_NAME | true | string | ∅ |
sso.oauth2[].default | Use as default | CDK_SSO_OAUTH2_0_DEFAULT | true | boolean | ∅ |
sso.oauth2[].client-id | OAuth2 client ID | CDK_SSO_OAUTH2_0_CLIENTID | true | string | ∅ |
sso.oauth2[].client-secret | OAuth2 client secret | CDK_SSO_OAUTH2_0_CLIENTSECRET | true | string | ∅ |
sso.oauth2[].openid.issuer | Issuer to check on token | CDK_SSO_OAUTH2_0_OPENID_ISSUER | true | string | ∅ |
sso.oauth2[].scopes | Scopes to be requested in the client credentials request | CDK_SSO_OAUTH2_0_SCOPES | true | string | [] |
sso.oauth2[].groups-claim | Group attribute from your identity provider | CDK_SSO_OAUTH2_0_GROUPSCLAIM | false | string | ∅ |
sso.oauth2[].username-claim | Email attribute from your identity provider | CDK_SSO_OAUTH2_0_USERNAMECLAIM | false | string | email |
sso.oauth2[].allow-unsigned-id-tokens | Allow unsigned ID tokens | CDK_SSO_OAUTH2_0_ALLOWUNSIGNEDIDTOKENS | false | boolean | false |
sso.oauth2[].preferred-jws-algorithm | Configure preferred JWS algorithm | CDK_SSO_OAUTH2_0_PREFERREDJWSALGORITHM | false | string one of: "HS256", "HS384", "HS512", "RS256", "RS384", "RS512", "ES256", "ES256K", "ES384", "ES512", "PS256", "PS384", "PS512", "EdDSA" | ∅ |
sso.oauth2-logout | Wether the central identity provider logout should be called or not | CDK_SSO_OAUTH2LOGOUT | false | boolean | true |
JWT auth properties
| Property | Description | Environment variable | Mandatory | Type | Default |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
sso.jwt-auth.issuer | Issuer of your identity provider | CDK_SSO_JWTAUTH_ISSUER | true | string | ∅ |
sso.jwt-auth.username-claim | Email attribute from your identity provider | CDK_SSO_JWTAUTH_USERNAMECLAIM | false | string | email |
sso.jwt-auth.groups-claim | Group attribute from your identity provider | CDK_SSO_JWTAUTH_GROUPSCLAIM | false | string | groups |
sso.jwt-auth.api-key-claim | API key attribute from your identity provider | CDK_SSO_JWTAUTH_APIKEYCLAIM | false | string | apikey |
Kafka cluster properties
The new recommended way to configure clusters is through the CLI and YAML manifests. Check KafkaCluster documentation for details.
For more information on configuring your Kafka clusters using GitOps processes, see GitOps: Managing Cluster configurations.
You can find sample configurations on the Configuration snippets page.
| Property | Description | Environment variable | Mandatory | Type | Default |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
clusters[].id | String used to uniquely identify your Kafka cluster | CDK_CLUSTERS_0_ID | true | string | ∅ |
clusters[].name | Alias or user-friendly name for your Kafka cluster | CDK_CLUSTERS_0_NAME | true | string | ∅ |
clusters[].color | Attach a color to associate with your cluster in the UI | CDK_CLUSTERS_0_COLOR | false | string in hexadecimal format (#FFFFFF) | random |
clusters[].ignoreUntrustedCertificate | Skip SSL certificate validation | CDK_CLUSTERS_0_IGNOREUNTRUSTEDCERTIFICATE | false | boolean | false |
clusters[].bootstrapServers | List of host:port for your Kafka brokers separated by coma , | CDK_CLUSTERS_0_BOOTSTRAPSERVERS | true | string | ∅ |
clusters[].properties | Any cluster configuration properties | CDK_CLUSTERS_0_PROPERTIES | false | string where each line is a property | ∅ |
Kafka vendor specific properties
Note that you only need to set the Kafka cluster properties to use the core features of Console.
However, you can get additional benefits by setting the flavor of your cluster. This corresponds to the Provider tab of your cluster configuration in Console.
| Property | Description | Environment variable | Mandatory | Type | Default |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
clusters[].kafkaFlavor.type | Kafka flavor type, one of Confluent, Aiven, Gateway | CDK_CLUSTERS_0_KAFKAFLAVOR_TYPE | false | string | ∅ |
Flavor is Confluent | Manage Confluent Cloud service accounts, API keys, and ACLs | ||||
clusters[].kafkaFlavor.key | Confluent Cloud API Key | CDK_CLUSTERS_0_KAFKAFLAVOR_KEY | true | string | ∅ |
clusters[].kafkaFlavor.secret | Confluent Cloud API Secret | CDK_CLUSTERS_0_KAFKAFLAVOR_SECRET | true | string | ∅ |
clusters[].kafkaFlavor.confluentEnvironmentId | Confluent Environment ID | CDK_CLUSTERS_0_KAFKAFLAVOR_CONFLUENTENVIRONMENTID | true | string | ∅ |
clusters[].kafkaFlavor.confluentClusterId | Confluent Cluster ID | CDK_CLUSTERS_0_KAFKAFLAVOR_CONFLUENTCLUSTERID | true | string | ∅ |
Flavor is Aiven | Manage Aiven service accounts and ACLs | ||||
clusters[].kafkaFlavor.apiToken | Aiven API token | CDK_CLUSTERS_0_KAFKAFLAVOR_APITOKEN | true | string | ∅ |
clusters[].kafkaFlavor.project | Aiven project | CDK_CLUSTERS_0_KAFKAFLAVOR_PROJECT | true | string | ∅ |
clusters[].kafkaFlavor.serviceName | Aiven service name | CDK_CLUSTERS_0_KAFKAFLAVOR_SERVICENAME | true | string | ∅ |
Flavor is Gateway | Manage Conduktor Gateway interceptors | ||||
clusters[].kafkaFlavor.url | Gateway API endpoint URL | CDK_CLUSTERS_0_KAFKAFLAVOR_URL | true | string | ∅ |
clusters[].kafkaFlavor.user | Gateway API username | CDK_CLUSTERS_0_KAFKAFLAVOR_USER | true | string | ∅ |
clusters[].kafkaFlavor.password | Gateway API password | CDK_CLUSTERS_0_KAFKAFLAVOR_PASSWORD | true | string | ∅ |
clusters[].kafkaFlavor.virtualCluster | Gateway virtual cluster | CDK_CLUSTERS_0_KAFKAFLAVOR_VIRTUALCLUSTER | true | string | ∅ |
Schema registry properties
| Property | Description | Environment variable | Mandatory | Type | Default |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
clusters[].schemaRegistry.url | The schema registry URL | CDK_CLUSTERS_0_SCHEMAREGISTRY_URL | true | string | ∅ |
clusters[].schemaRegistry.ignoreUntrustedCertificate | Skip SSL certificate validation | CDK_CLUSTERS_0_SCHEMAREGISTRY_IGNOREUNTRUSTEDCERTIFICATE | false | boolean | false |
clusters[].schemaRegistry.properties | Any schema registry configuration parameters | CDK_CLUSTERS_0_SCHEMAREGISTRY_PROPERTIES | false | string where each line is a property | ∅ |
| Basic Authentication | |||||
clusters[].schemaRegistry.security.username | Basic auth username | CDK_CLUSTERS_0_SCHEMAREGISTRY_SECURITY_USERNAME | false | string | ∅ |
clusters[].schemaRegistry.security.password | Basic auth password | CDK_CLUSTERS_0_SCHEMAREGISTRY_SECURITY_PASSWORD | false | string | ∅ |
| Bearer Token Authentication | |||||
clusters[].schemaRegistry.security.token | Bearer auth token | CDK_CLUSTERS_0_SCHEMAREGISTRY_SECURITY_TOKEN | false | string | ∅ |
| mTLS Authentication | |||||
clusters[].schemaRegistry.security.key | Access Key | CDK_CLUSTERS_0_SCHEMAREGISTRY_SECURITY_KEY | false | string | ∅ |
clusters[].schemaRegistry.security.certificateChain | Access certificate | CDK_CLUSTERS_0_SCHEMAREGISTRY_SECURITY_CERTIFICATECHAIN | false | string | ∅ |
Amazon Glue schema registry properties
| Property | Description | Environment variable | Mandatory | Type | Default |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
clusters[].schemaRegistry.region | The Glue schema registry region | CDK_CLUSTERS_0_SCHEMAREGISTRY_REGION | true | string | ∅ |
clusters[].schemaRegistry.registryName | The Glue schema registry name | CDK_CLUSTERS_0_SCHEMAREGISTRY_REGISTRYNAME | false | string | ∅ |
clusters[].schemaRegistry.amazonSecurity.type | Authentication with credentials, one of Credentials, FromContext, FromRole | CDK_CLUSTERS_0_SCHEMAREGISTRY_AMAZONSECURITY_TYPE | true | string | ∅ |
| Credentials Security | |||||
clusters[].schemaRegistry.amazonSecurity.accessKeyId | Credentials auth access key | CDK_CLUSTERS_0_SCHEMAREGISTRY_AMAZONSECURITY_ACCESSKEYID | true | string | ∅ |
clusters[].schemaRegistry.amazonSecurity.secretKey | Credentials auth secret key | CDK_CLUSTERS_0_SCHEMAREGISTRY_AMAZONSECURITY_SECRETKEY | true | string | ∅ |
| FromContext Security | |||||
clusters[].schemaRegistry.amazonSecurity.profile | Authentication profile | CDK_CLUSTERS_0_SCHEMAREGISTRY_AMAZONSECURITY_PROFILE | false | string | ∅ |
| FromRole Security | |||||
clusters[].schemaRegistry.amazonSecurity.role | Authentication role | CDK_CLUSTERS_0_SCHEMAREGISTRY_AMAZONSECURITY_ROLE | true | string | ∅ |
Kafka Connect properties
| Property | Description | Environment variable | Mandatory | Type | Default |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
clusters[].kafkaConnects[].id | String used to uniquely identify your Kafka Connect | CDK_CLUSTERS_0_KAFKACONNECTS_0_ID | true | string | ∅ |
clusters[].kafkaConnects[].name | Name your Kafka Connect | CDK_CLUSTERS_0_KAFKACONNECTS_0_NAME | true | string | ∅ |
clusters[].kafkaConnects[].url | The Kafka connect URL | CDK_CLUSTERS_0_KAFKACONNECTS_0_URL | true | string | ∅ |
clusters[].kafkaConnects[].headers | Optional additional headers (ie: X-API-Token=123,X-From=Test) | CDK_CLUSTERS_0_KAFKACONNECTS_0_HEADERS | false | string | ∅ |
clusters[].kafkaConnects[].ignoreUntrustedCertificate | Skip SSL certificate validation | CDK_CLUSTERS_0_KAFKACONNECTS_0_IGNOREUNTRUSTEDCERTIFICATE | false | boolean | false |
| Basic Authentication | |||||
clusters[].kafkaConnects[].security.username | Basic auth username | CDK_CLUSTERS_0_KAFKACONNECTS_0_SECURITY_USERNAME | false | string | ∅ |
clusters[].kafkaConnects[].security.password | Basic auth password | CDK_CLUSTERS_0_KAFKACONNECTS_0_SECURITY_PASSWORD | false | string | ∅ |
| Bearer Token Authentication | |||||
clusters[].kafkaConnects[].security.token | Bearer token | CDK_CLUSTERS_0_KAFKACONNECTS_0_SECURITY_TOKEN | false | string | ∅ |
| mTLS Authentication | |||||
clusters[].kafkaConnects[].security.key | Access key | CDK_CLUSTERS_0_KAFKACONNECTS_0_SECURITY_KEY | false | string | ∅ |
clusters[].kafkaConnects[].security.certificateChain | Access certificate | CDK_CLUSTERS_0_KAFKACONNECTS_0_SECURITY_CERTIFICATECHAIN | false | string | ∅ |
ksqlDB properties
We support ksqlDB integration as of Conduktor Console v1.21.0.
| Property | Description | Environment variable | Mandatory | Type | Default |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
clusters[].ksqlDBs[].id | String used to uniquely identify your ksqlDB Cluster | CDK_CLUSTERS_0_KSQLDBS_0_ID | true | string | ∅ |
clusters[].ksqlDBs[].name | Name of your ksqlDB Cluster | CDK_CLUSTERS_0_KSQLDBS_0_NAME | true | string | ∅ |
clusters[].ksqlDBs[].url | The ksqlDB API URL | CDK_CLUSTERS_0_KSQLDBS_0_URL | true | string | ∅ |
clusters[].ksqlDBs[].ignoreUntrustedCertificate | Skip SSL certificate validation | CDK_CLUSTERS_0_KSQLDBS_0_IGNOREUNTRUSTEDCERTIFICATE | false | boolean | false |
| Basic Authentication | |||||
clusters[].ksqlDBs[].security.username | Basic auth username | CDK_CLUSTERS_0_KSQLDBS_0_SECURITY_USERNAME | false | string | ∅ |
clusters[].ksqlDBs[].security.password | Basic auth password | CDK_CLUSTERS_0_KSQLDBS_0_SECURITY_PASSWORD | false | string | ∅ |
| Bearer Token Authentication | |||||
clusters[].ksqlDBs[].security.token | Bearer token | CDK_CLUSTERS_0_KSQLDBS_0_SECURITY_TOKEN | false | string | ∅ |
| mTLS Authentication | |||||
clusters[].ksqlDBs[].security.key | Access key | CDK_CLUSTERS_0_KSQLDBS_0_SECURITY_KEY | false | string | ∅ |
clusters[].ksqlDBs[].security.certificateChain | Access certificate | CDK_CLUSTERS_0_KSQLDBS_0_SECURITY_CERTIFICATECHAIN | false | string | ∅ |
Indexer properties
The indexer is the internal process of Conduktor Console that fetches metadata from your Kafka cluster (e.g. topics, consumer groups, subjects). You should modify these parameters only if you see an issue with the performance of the indexer.
| Property | Description | Environment variable | Mandatory | Type | Default |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lag exporter | |||||
lagexporter.frequency | Frequency in seconds of the execution of the lag exporter | CDK_LAGEXPORTER_FREQUENCY | false | int | 30 |
lagexporter.clusterparallelism | Number of clusters indexed in parallel for the lag exporter | CDK_LAGEXPORTER_CLUSTERPARALLELISM | false | int | 1 |
lagexporter.indexertimeout | Lag exporter timeout in seconds | CDK_LAGEXPORTER_INDEXERTIMEOUT | false | int | 300 (5 minutes) |
| Metadata indexer | |||||
metadataindexer.frequency | Frequency in seconds of the execution of the metadata indexer | CDK_METADATAINDEXER_FREQUENCY | false | int | 30 |
metadataindexer.clusterparallelism | Number of clusters indexed in parallel for the metadata indexer | CDK_METADATAINDEXER_CLUSTERPARALLELISM | false | int | 1 |
metadataindexer.indexertimeout | Metadata indexer timeout in seconds | CDK_METADATAINDEXER_INDEXERTIMEOUT | false | int | 300 (5 minutes) |
| Monitoring indexer | |||||
monitoringconfig.frequency | Frequency in seconds of the execution of the monitoring indexer | CDK_MONITORINGCONFIG_FREQUENCY | false | int | 30 |
monitoringconfig.clusterparallelism | Number of clusters indexed in parallel for the monitoring indexer | CDK_MONITORINGCONFIG_CLUSTERPARALLELISM | false | int | 1 |
monitoringconfig.indexertimeout | Monitoring indexer timeout in seconds | CDK_MONITORINGCONFIG_INDEXERTIMEOUT | false | int | 300 (5 minutes) |
| Schema registry indexer | |||||
registryindexer.frequency | Frequency in seconds of the execution of the schema registry indexer | CDK_REGISTRYINDEXER_FREQUENCY | false | int | 30 |
registryindexer.clusterparallelism | Number of clusters indexed in parallel for the schema registry indexer | CDK_REGISTRYINDEXER_CLUSTERPARALLELISM | false | int | 1 |
registryindexer.indexertimeout | Schema registry indexer timeout in seconds | CDK_REGISTRYINDEXER_INDEXERTIMEOUT | false | int | 300 (5 minutes) |
| Kafka connect indexer | |||||
connectindexer.frequency | Frequency in seconds of the execution of the kafka connect indexer | CDK_CONNECTINDEXER_FREQUENCY | false | int | 30 |
connectindexer.clusterparallelism | Number of clusters indexed in parallel for the kafka connect indexer | CDK_CONNECTINDEXER_CLUSTERPARALLELISM | false | int | 1 |
connectindexer.indexertimeout | Kafka connect indexer timeout in seconds | CDK_CONNECTINDEXER_INDEXERTIMEOUT | false | int | 300 (5 minutes) |
| Kafka admin client configuration | |||||
kafka_admin.list_consumer_group_offsets_batch_size | How many consumer groups offset to fetch in a single query. Old versions of Kafka may time out when fetching too many offsets at once. | CDK_KAFKAADMIN_LISTCONSUMERGROUPOFFSETSBATCHSIZE | false | int | 100 |
kafka_admin.batch_parallel_size | Maximum of batched requests that can be sent in parallel | CDK_KAFKAADMIN_BATCHPARALLELSIZE | false | int | 5 |
kafka_admin.record_size_limit | Maximum size in bytes of a single message to display in the consume page. For larger messages, you'll get a link to open in a dedicated page. | CDK_KAFKAADMIN_RECORDSIZELIMIT | false | int | 102400 (bytes) |
AuditLog export properties
The audit log can be exported to a Kafka topic, once configured in Console. For details on the available exportable events refer to: Exportable audit log events.
| Property | Description | Environment variable | Mandatory | Type | Default |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
audit_log_publisher.cluster | The cluster ID where the audit logs will be exported | CDK_AUDITLOGPUBLISHER_CLUSTER | false | string | ∅ |
audit_log_publisher.topicName | The topic name where the audit logs will be exported | CDK_AUDITLOGPUBLISHER_TOPICNAME | false | string | ∅ |
audit_log_publisher.topicConfig.partition | The number of partitions for the audit log topic | CDK_AUDITLOGPUBLISHER_TOPICCONFIG_PARTITION | false | int | 1 |
audit_log_publisher.topicConfig.replicationFactor | The replication factor for the audit log topic | CDK_AUDITLOGPUBLISHER_TOPICCONFIG_REPLICATIONFACTOR | false | int | 1 |
Conduktor SQL properties
In order to use Conduktor SQL, you need to configure a second database to store the topics data.
You can configure Conduktor SQL Database using CDK_KAFKASQL_DATABASE_URL or set each value individually with CDK_KAFKASQL_DATABASE_*.
| Property | Description | Environment variable | Mandatory | Type | Default |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
kafka_sql.database.url | External PostgreSQL configuration URL in format [jdbc:]postgresql://[user[:password]@][[netloc][:port],...][/dbname][?param1=value1&...] | CDK_KAFKASQL_DATABASE_URL | false | string | ∅ |
kafka_sql.database.hosts[].host | External PostgreSQL servers hostname | CDK_KAFKASQL_DATABASE_HOSTS_0_HOST | false | string | ∅ |
kafka_sql.database.hosts[].port | External PostgreSQL servers port | CDK_KAFKASQL_DATABASE_HOSTS_0_PORT | false | int | ∅ |
kafka_sql.database.host | External PostgreSQL server hostname (Deprecated, use kafka_sql.database.hosts instead) | CDK_KAFKASQL_DATABASE_HOST | false | string | ∅ |
kafka_sql.database.port | External PostgreSQL server port (Deprecated, use kafka_sql.database.hosts instead) | CDK_KAFKASQL_DATABASE_PORT | false | int | ∅ |
kafka_sql.database.name | External PostgreSQL database name | CDK_KAFKASQL_DATABASE_NAME | false | string | ∅ |
kafka_sql.database.username | External PostgreSQL login role | CDK_KAFKASQL_DATABASE_USERNAME | false | string | ∅ |
kafka_sql.database.password | External PostgreSQL login password | CDK_KAFKASQL_DATABASE_PASSWORD | false | string | ∅ |
kafka_sql.database.connection_timeout | External PostgreSQL connection timeout in seconds | CDK_KAFKASQL_DATABASE_CONNECTIONTIMEOUT | false | int | ∅ |
Advanced properties:
| Property | Description | Environment variable | Mandatory | Type | Default |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
kafka_sql.commit_offset_every_in_sec | Frequency at which Conduktor SQL commits offsets into Kafka and flushes rows in the database | CDK_KAFKASQL_COMMITOFFSETEVERYINSEC | false | int | 30 (seconds) |
kafka_sql.clean_expired_record_every_in_hour | How often to check for expired records and delete them from the database | CDK_KAFKASQL_CLEANEXPIREDRECORDEVERYINHOUR | false | int | 1 (hour) |
kafka_sql.refresh_topic_configuration_every_in_sec | Frequency at which Conduktor SQL looks for new topics to start indexing or stop indexing | CDK_KAFKASQL_REFRESHTOPICCONFIGURATIONEVERYINSEC | false | int | 30 (seconds) |
kafka_sql.consumer_group_id | Consumer group used to identify Conduktor SQL | CDK_KAFKASQL_CONSUMER-GROUP-ID | false | string | conduktor-sql |
kafka_sql.refresh_user_permissions_every_in_sec | Frequency at which Conduktor SQL refreshes the role permissions in the DB to match the RBAC setup in Console | CDK_KAFKASQL_REFRESHUSERPERMISSIONSEVERYINSEC | false | string | conduktor-sql |
Partner Zones properties
Advanced configuration for Partner Zones.
| Property | Description | Environment variable | Mandatory | Type | Default |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
partner_zone.reconcile-with-gateway-every-seconds | The interval at which Partner Zone's state (that's stored on Console) is synchronized with Gateway. A lower value results in faster alignment between the required state and the current state on the Gateway. | CDK_PARTNERZONE_RECONCILEWITHGATEWAYEVERYSECONDS | false | int | 5 (seconds) |
Configure HTTP proxy
Specify the proxy settings for Conduktor to use when accessing Internet. The HTTP proxy works for both HTTP and HTTPS connection.
There are five properties you can set to specify the proxy that will be used by the HTTP protocol handler:
CDK_HTTP_PROXY_HOST: the host name of the proxy serverCDK_HTTP_PROXY_PORT: the port number. Default value is 80.CDK_HTTP_NON_PROXY_HOSTS: a list of hosts that should be reached directly, bypassing the proxy. This is a list of patterns separated by|. The patterns may start or end with a*for wildcards, we do not support/. Any host matching one of these patterns will be reached through a direct connection instead of through a proxy.CDK_HTTP_PROXY_USERNAME: the proxy usernameCDK_HTTP_PROXY_PASSWORD: the proxy password
Example
services:
conduktor-console:
image: conduktor/conduktor-console
ports:
- 8080:8080
environment:
CDK_HTTP_PROXY_HOST: "proxy.mydomain.com"
CDK_HTTP_PROXY_PORT: 8000
CDK_HTTP_NON_PROXY_HOSTS: "*.mydomain.com"
Configure HTTPS
To configure Conduktor Console to respond to HTTPS requests, you have to define a certificate and a private key.
The server certificate is a public entity that's sent to every client that connects to the server and it should be provided as a PEM file.
Configuration properties are:
platform.https.cert.pathor environment variableCDK_PLATFORM_HTTPS_CERT_PATH: the path to server certificate fileplatform.https.key.pathor environment variableCDK_PLATFORM_HTTPS_KEY_PATH: the path to server private key file
Both the certificate and private key files have to allow read from user conduktor-platform (UID 10001 GID 0) but don't need to be readable system-wide.
Sample configuration using docker-compose
In this example, server certificate and key (server.crt and server.key) are stored in the same directory as the docker-compose file.
services:
conduktor-console:
image: conduktor/conduktor-console
ports:
- 8080:8080
volumes:
- type: bind
source: ./server.crt
target: /opt/conduktor/certs/server.crt
read_only: true
- type: bind
source: ./server.key
target: /opt/conduktor/certs/server.key
read_only: true
environment:
CDK_PLATFORM_HTTPS_CERT_PATH: '/opt/conduktor/certs/server.crt'
CDK_PLATFORM_HTTPS_KEY_PATH: '/opt/conduktor/certs/server.key'
If the monitoring image conduktor/conduktor-console-cortex is running as well, you have to provide the CA public certificate to the monitoring image to allow metrics scraping on HTTPS.
services:
conduktor-console:
image: conduktor/conduktor-console
ports:
- 8080:8080
volumes:
- type: bind
source: ./server.crt
target: /opt/conduktor/certs/server.crt
read_only: true
- type: bind
source: ./server.key
target: /opt/conduktor/certs/server.key
read_only: true
environment:
# HTTPS configuration
CDK_PLATFORM_HTTPS_CERT_PATH: '/opt/conduktor/certs/server.crt'
CDK_PLATFORM_HTTPS_KEY_PATH: '/opt/conduktor/certs/server.key'
# monitoring configuration
CDK_MONITORING_CORTEX-URL: http://conduktor-monitoring:9009/
CDK_MONITORING_ALERT-MANAGER-URL: http://conduktor-monitoring:9010/
CDK_MONITORING_CALLBACK-URL: https://conduktor-console:8080/monitoring/api/
CDK_MONITORING_NOTIFICATIONS-CALLBACK-URL: http://localhost:8080
conduktor-monitoring:
image: conduktor/conduktor-console-cortex
volumes:
- type: bind
source: ./server.crt
target: /opt/conduktor/certs/server.crt
read_only: true
environment:
CDK_CONSOLE-URL: "https://conduktor-console:8080"
CDK_SCRAPER_SKIPSSLCHECK: "false" # can be set to true if you don't want to check the certificate
CDK_SCRAPER_CAFILE: "/opt/conduktor/certs/server.crt"